For all examples, so-called re-branding was used, which means that the design of all messages, emails or websites is adapted to the design of our company. This plays no role in the correctness of the answers. Questions may have one or more correct answers.
---
primary_color: '#00e1c6'
secondary_color: '#afbac4'
text_color: '#292F36'
shuffle_questions: false
---
## Facebook
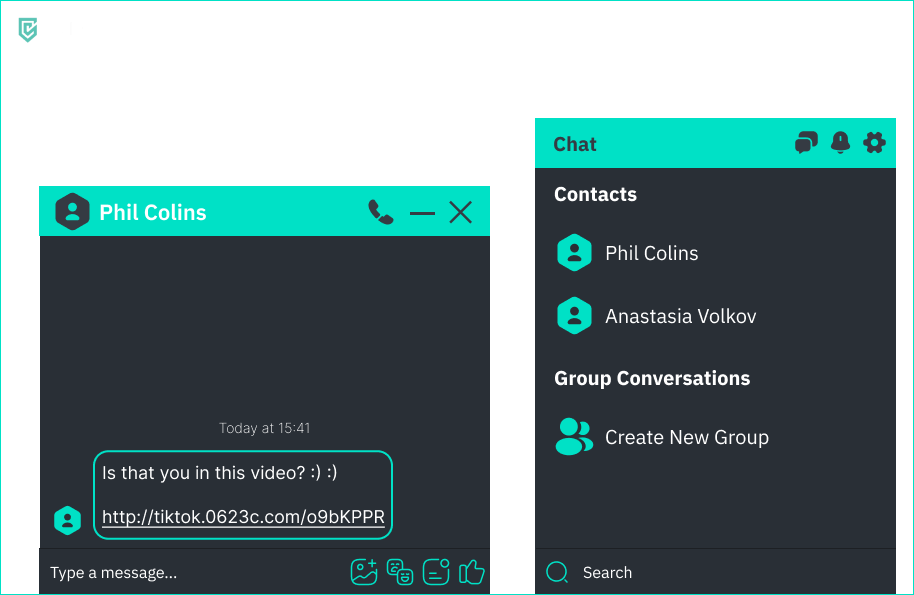
Is this message dangerous? > Is this a real URL? Is the HTTP protocol secure? - [x] Yes, because the url is fake. - [ ] Yes, because I didn't get a notification. - [ ] No, because Phil is my friend and would never send me an unsafe message. - [ ] No, because this is how a normal tiktok link looks like. ## Received email after online shopping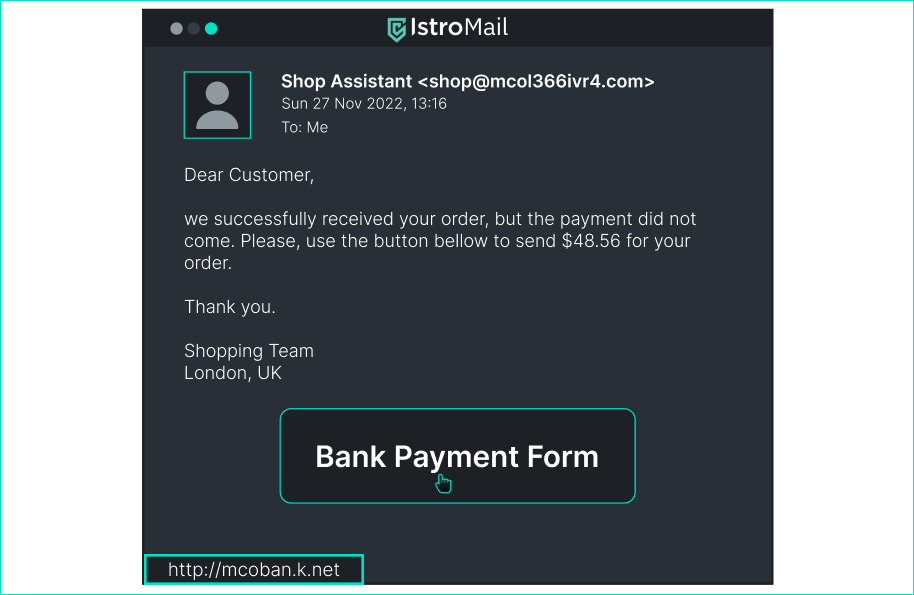
Is this email dangerous? > Always check the domain for emails. The domain can be found in the web address (bottom left) and also in the email address. - [x] Yes, because the button to the payment form leads to an insecure page. - [x] Yes, because the domain of the sender's email address definitely does not belong to the store. - [ ] No, because this is the email I get whenever I shop online. - [ ] No, because the email is signed by the sales team in London. ## Email for tracking your orded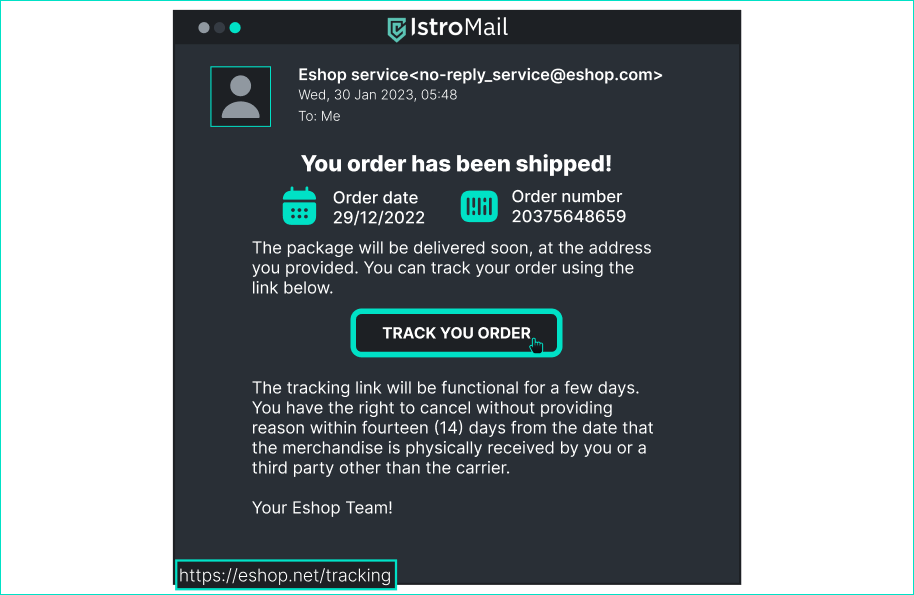
Is this email dangerous? > In auto-reply emails, companies often use "no-reply" names to let the recipient know not to reply. The URL looks equally legitimate because it uses the secure HTTPS protocol. - [ ] Yes, because the email didn't come to me from a specific employee. - [ ] Yes, because the button to track the mail leads to an unsafe web page. - [x] No, this email is legitimate. ## Instagram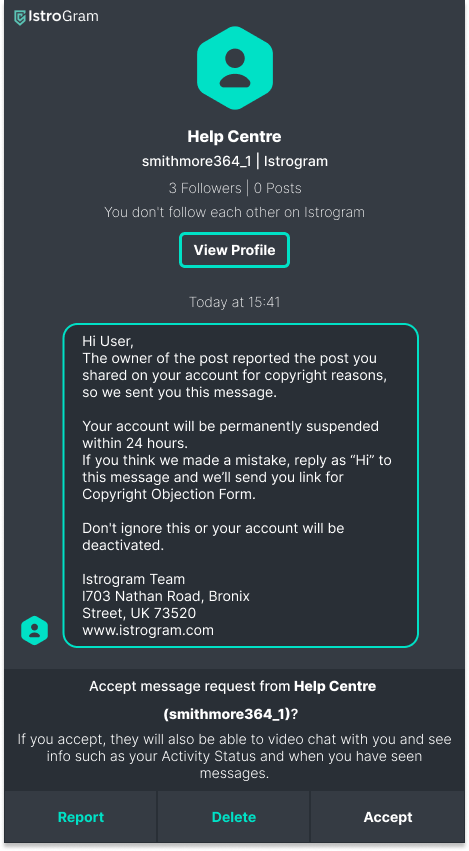
Is this message dangerous? > Do you consider a user with 3 followers, 0 posts to be a legitimate Help Center on such a platform? By what signs can a phishing message be recognized? - [x] Yes, because the account name and the name that appear in the message do not match clearly. - [x] Yes, there are clear signs of phishing in the message such as urgency and an attempt to give the impression that it is a legitimate sender (address, signature). - [ ] No, because the message is signed properly by the company's employees.. - [ ] No, because it is an automatically generated message from the Help Center. ## Email from your bank about new features in the app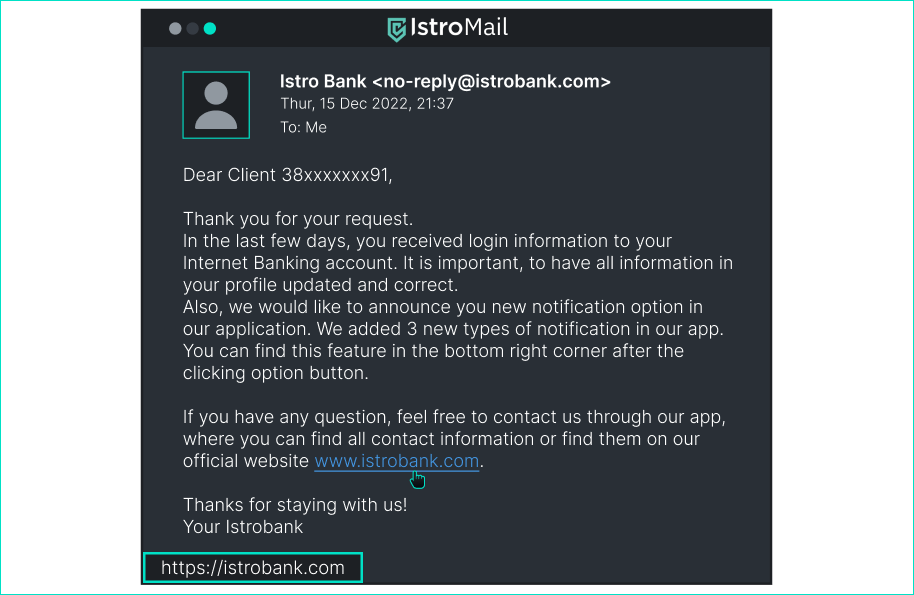
> In this case, the content of the email is very important. After reading it, think about what the attacker could gain from the email. - [ ] Yes, because the content of the email is trying to find out confidential personal information. - [ ] Yes, because the URL leads to a malicious site. - [x] No, because both the content and the click-through to another site are secure. - [ ] No, because I trust my bank. ## TikTok login website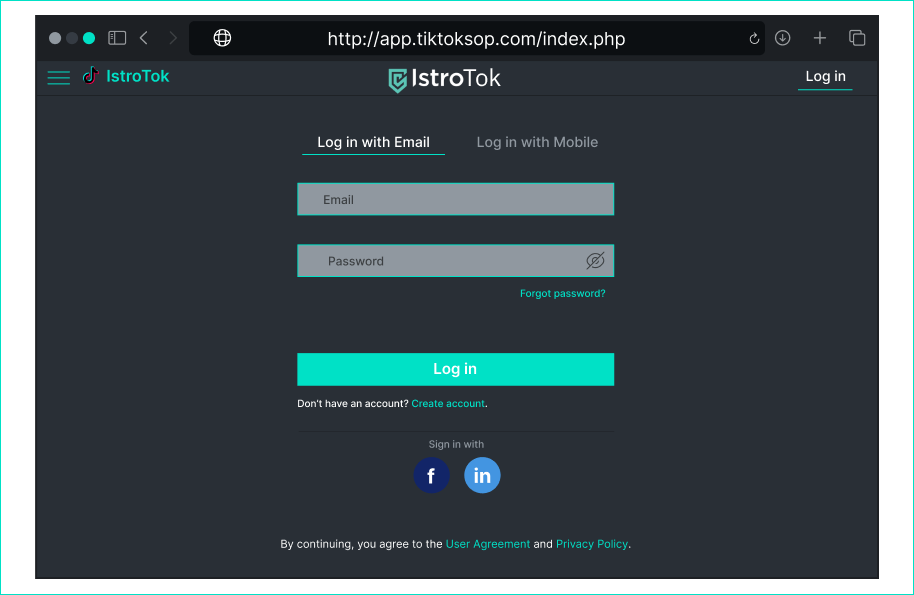
Is this website dangerous? > Have you looked at the URL? - [x] Yes, because this is not a legitimate URL for this platform. - [ ] No, because the design of the page looks original. - [ ] No, because I log in through this web all the time. ## Email for Netflix payment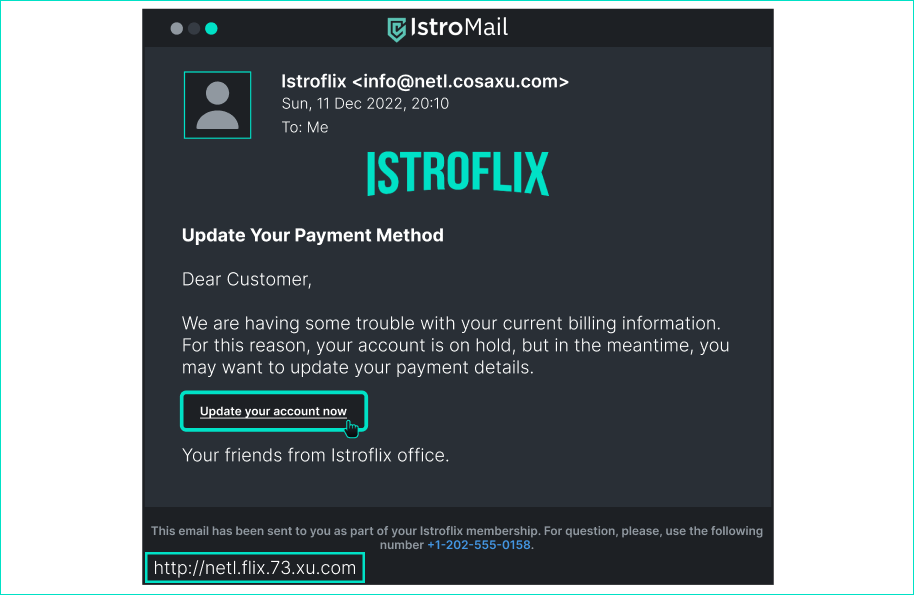
Is this email dangerous? > What is the domain in the email address and the website that the button takes you to? What certificate does this website use? Is one of the signs of phishing the urgency of the message? - [x] Yes, because the domain used in the email and the website, the email is supposed to redirect us to, is not the domain of the original platform. - [x] Yes, because the HTTP certificate is insecure. - [x] Yes, because the urgency and genericness of the email are clear signs of phishing. - [ ] No, because I get such an email every time I forget to pay. - [ ] No, because the email is carefully formatted using a logo. ## Eshop website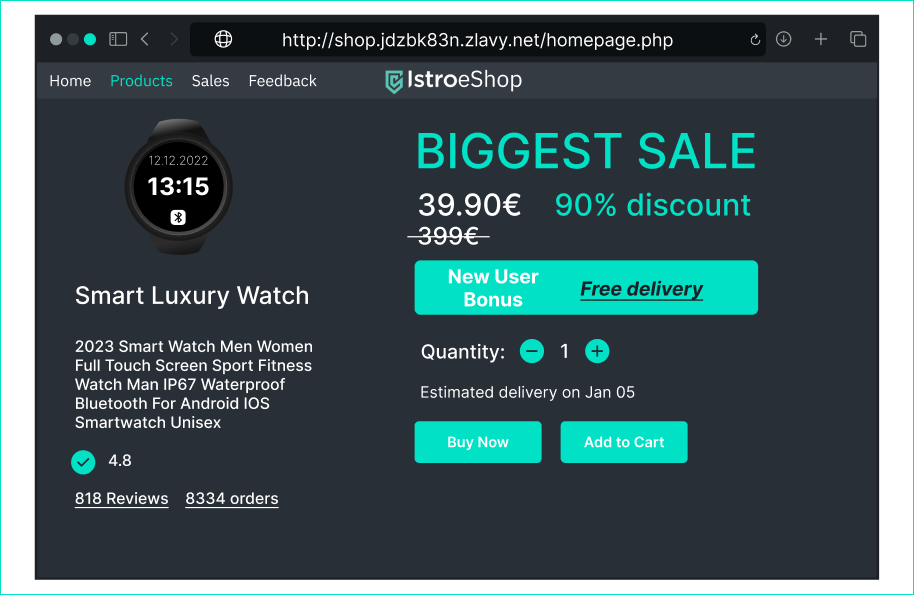
Is this website dangerous? > Are such huge discounts common? Did you notice the URL? - [x] Yes, because the site does not use HTTPS protocol. - [x] Yes, the domain of the URL is obviously unsafe. - [x] Yes, because such big discounts are dangerous. - [ ] No, because I shop at such eshops all the time. - [ ] No, because this product has many reviews and orders. ## Email from your transport service to fill the form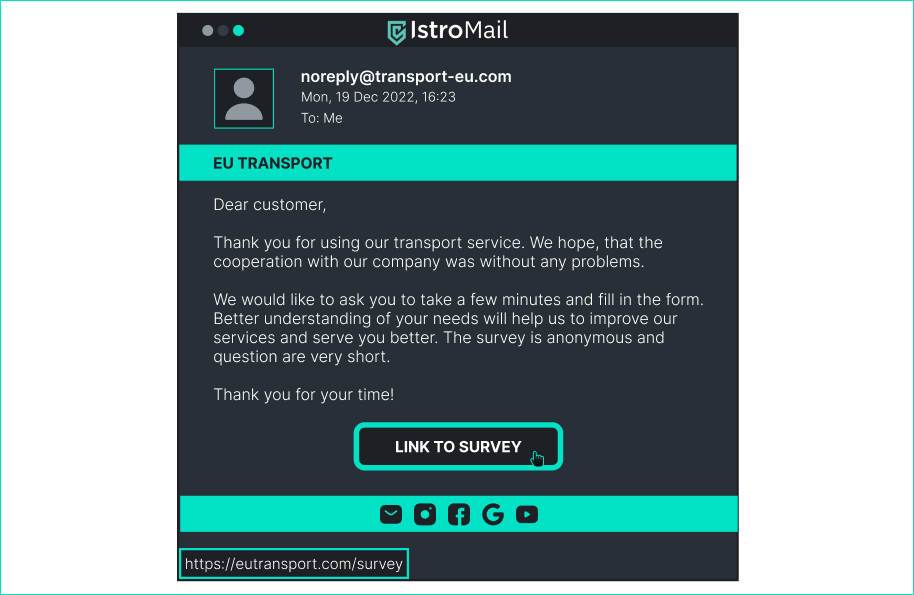
Is this email dangerous? > What does the HTTPS certificate say? Does the sender want to get something from us in the content? - [ ] Yes, because he is trying to get confidential information from us. - [ ] Yes, because the button takes us to an unsafe site. - [ ] Yes, because the email didn't come from the actual sender. - [x] No, because the content of the email does not indicate anything suspicious. - [x] No, because the button takes us to a legitimate website. ## Instagram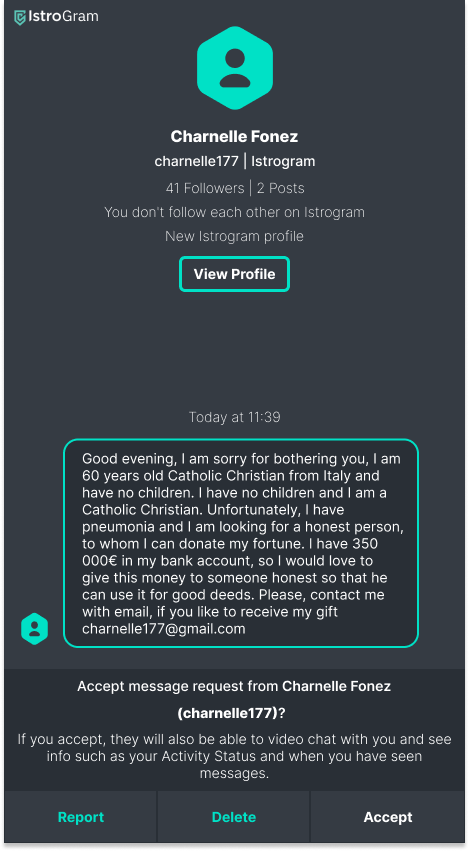
> The content of this report is clearly trying to give the impression of easy money. Where can such communication go? - [x] Yes, the content of this message clearly indicates that this is an attempt to scam. - [ ] No, it is just an elderly gentleman from Italy who wants to give money to some good people. - [ ] No, because enough people are following this person for me to trust him.

Is this message dangerous? > Is this a real URL? Is the HTTP protocol secure? - [x] Yes, because the url is fake. - [ ] Yes, because I didn't get a notification. - [ ] No, because Phil is my friend and would never send me an unsafe message. - [ ] No, because this is how a normal tiktok link looks like. ## Received email after online shopping

Is this email dangerous? > Always check the domain for emails. The domain can be found in the web address (bottom left) and also in the email address. - [x] Yes, because the button to the payment form leads to an insecure page. - [x] Yes, because the domain of the sender's email address definitely does not belong to the store. - [ ] No, because this is the email I get whenever I shop online. - [ ] No, because the email is signed by the sales team in London. ## Email for tracking your orded

Is this email dangerous? > In auto-reply emails, companies often use "no-reply" names to let the recipient know not to reply. The URL looks equally legitimate because it uses the secure HTTPS protocol. - [ ] Yes, because the email didn't come to me from a specific employee. - [ ] Yes, because the button to track the mail leads to an unsafe web page. - [x] No, this email is legitimate. ## Instagram

Is this message dangerous? > Do you consider a user with 3 followers, 0 posts to be a legitimate Help Center on such a platform? By what signs can a phishing message be recognized? - [x] Yes, because the account name and the name that appear in the message do not match clearly. - [x] Yes, there are clear signs of phishing in the message such as urgency and an attempt to give the impression that it is a legitimate sender (address, signature). - [ ] No, because the message is signed properly by the company's employees.. - [ ] No, because it is an automatically generated message from the Help Center. ## Email from your bank about new features in the app

> In this case, the content of the email is very important. After reading it, think about what the attacker could gain from the email. - [ ] Yes, because the content of the email is trying to find out confidential personal information. - [ ] Yes, because the URL leads to a malicious site. - [x] No, because both the content and the click-through to another site are secure. - [ ] No, because I trust my bank. ## TikTok login website

Is this website dangerous? > Have you looked at the URL? - [x] Yes, because this is not a legitimate URL for this platform. - [ ] No, because the design of the page looks original. - [ ] No, because I log in through this web all the time. ## Email for Netflix payment

Is this email dangerous? > What is the domain in the email address and the website that the button takes you to? What certificate does this website use? Is one of the signs of phishing the urgency of the message? - [x] Yes, because the domain used in the email and the website, the email is supposed to redirect us to, is not the domain of the original platform. - [x] Yes, because the HTTP certificate is insecure. - [x] Yes, because the urgency and genericness of the email are clear signs of phishing. - [ ] No, because I get such an email every time I forget to pay. - [ ] No, because the email is carefully formatted using a logo. ## Eshop website

Is this website dangerous? > Are such huge discounts common? Did you notice the URL? - [x] Yes, because the site does not use HTTPS protocol. - [x] Yes, the domain of the URL is obviously unsafe. - [x] Yes, because such big discounts are dangerous. - [ ] No, because I shop at such eshops all the time. - [ ] No, because this product has many reviews and orders. ## Email from your transport service to fill the form

Is this email dangerous? > What does the HTTPS certificate say? Does the sender want to get something from us in the content? - [ ] Yes, because he is trying to get confidential information from us. - [ ] Yes, because the button takes us to an unsafe site. - [ ] Yes, because the email didn't come from the actual sender. - [x] No, because the content of the email does not indicate anything suspicious. - [x] No, because the button takes us to a legitimate website. ## Instagram

> The content of this report is clearly trying to give the impression of easy money. Where can such communication go? - [x] Yes, the content of this message clearly indicates that this is an attempt to scam. - [ ] No, it is just an elderly gentleman from Italy who wants to give money to some good people. - [ ] No, because enough people are following this person for me to trust him.